Yesterday, SNH published the following press release:
General licences restricted in wildlife crime hotspots
Scottish Natural Heritage (SNH) has restricted the use of general licences on four properties in two wildlife crime hotspots – one in Stirlingshire and one in the Borders – this week. The decision was made on the basis of evidence provided by Police Scotland of wildlife crime against birds.
Nick Halfhide, SNH Director of Operations, said:
“There is clear evidence that wildlife crimes have been committed on these properties. Because of this, and the risk of more wildlife crimes taking place, we have suspended the general licences on these four properties for three years. They may though still apply for individual licences, but these will be closely monitored.
“This measure should help to protect wild birds in the area, while still allowing necessary land management activities to take place, albeit under tighter supervision. We consider that this is a proportionate response to protect wild birds in the area and prevent further wildlife crime.”
General licences allow landowners or land managers to carry out actions which would otherwise be illegal, including controlling common species of wild birds to protect crops or livestock.
The new measure complements other recent actions to reduce wildlife crime, including vicarious liability for offences against wild birds, which was introduced in 2011.
Restrictions will prevent people from using the general licences on the land in question for three years. This period will increase if more evidence of offences comes to light.
END
As promised in earlier correspondence with SNH about potential General Licence restrictions (e.g. see here), SNH has published ‘details’ of the current restrictions on its website. Although when we say ‘details’ we use the term loosely. The names of the estates have not been published (but see below) and the specific reasons (crimes) that triggered the restriction orders are also absent.
Instead, SNH has published two maps showing the areas where the three-year restriction orders will be in place.
Restriction order #1 can be viewed here: GL restriction order 1_ Nov 2015-2018
The map denoting the area relating to Restriction order #1 is here:

Having consulted Andy Wightman’s brilliant website Who Owns Scotland to check estate boundaries, we now know that the delineated area shown in Restriction order #1 includes parts of Raeshaw Estate and the neighbouring Corsehope Estate.
This is fascinating. Raeshaw Estate is well known to us and continues to be of interest. It is a mixed upland estate combining driven grouse shooting as well as pheasant and partridge shooting. We have documentary evidence that Mark Osborne’s company is involved in the estate management (more on that in the near future). Raeshaw Estate has been raided by the police at least twice (2004 and 2009 – poisoned and shot raptors and poisoned baits – see here) although nobody has ever been prosecuted for these crimes. However, the General Licence Restriction can only be applied for crimes that have been uncovered since 1st January 2014; it cannot be applied retrospectively for offences that took place prior to 1st January 2014. This means that further raptor crimes have been uncovered here but there has not been any publicity about them. Why not? There was news of a shot buzzard found in the nearby area on 24th July 2015 (see here), but this bird was found AFTER SNH had notified the estate of the intention to restrict the General Licence (see here) so this incident cannot be the one that triggered the General Licence Restriction.
Corsehope Estate has not been on our radar, although we’re told by local sources that gamekeepers from Raeshaw Estate are involved with ‘vermin control’ here so now we’re very interested.
Restriction order #2 can be viewed here: GL retriction order 2_ Nov 2015-2018
The map denoting the area relating to Restriction order #2 is here:
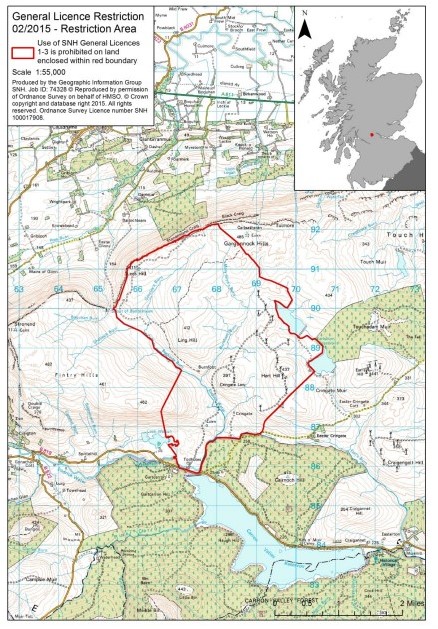
Again, consulting Andy Wightman’s excellent website Who Owns Scotland to check estate boundaries, we now know that the delineated area shown in Restriction order #2 includes parts of Burnfoot Estate and Wester Cringate Estate.
This is also interesting. We believe (although it must be stressed that this is educated speculation as SNH has not published the information) that this restriction order probably relates to a series of raptor persecution crimes including a poisoned red kite (July 2014), a poisoned peregrine (February 2015) and an illegally trapped red kite (May 2015) – see here.
So, what do these General Licence Restriction orders mean? Basically, it means that the following activities, usually permitted under General Licences 1, 2 and 3, are now not permitted in the areas shown on the two maps for three years, starting 13th November 2015 and ending 12th November 2018:
The killing or taking of the following species:
Great black-backed gull, carrion crow, hooded crow, jackdaw, jay, rook, ruddy duck, magpie, Canada goose, collared dove, feral pigeon, wood pigeon, lesser black-back gull, and herring gull.
The use of the following methods to kill/take these species are not permitted:
Pricking of eggs, oiling of eggs, destruction of eggs and nests, use of Larsen trap, use of Larsen Mate trap, use of Larsen Pod trap, use of multi-catch crow cage trap, shooting with any firearm, targeted falconry, and by hand.
That sounds great, doesn’t it? But it’s not quite as clear cut as that. As we’ve discussed before, and as is stated in the SNH press release at the top of this blog, although these activities can no longer be carried out in the two denoted areas under the cover of the three General Licences, individuals may still apply for an individual licence to permit these activities, although SNH claims that if granted, these will be “closely monitored”.
What does ‘closely monitored’ actually mean? Closely monitored by whom? Daily inspections by SNH? Police Scotland? That’s hardly going to happen, is it?
Let’s hope that members of the general public, exercising their right to visit these areas under open access legislation, pay close attention to what’s going on around them. If they see a Larsen trap in use, or a crow cage trap in use, or witness any of the above bird species being killed/taken by any of the methods mentioned above, they inform the Police straight away. Actually, let’s hope they forget the police and inform RSPB Scotland and/or the SSPCA instead – they’re more likely to get a quick response from them.
It’ll be interesting to see how this all pans out. On the one hand, we welcome these Restriction orders and applaud the Scottish Government (especially former Environment Minister Paul Wheelhouse for initiating them), SNH and Police Scotland for pursuing what we hope will be the first of many such Restriction orders. But on the other hand, will these restrictions be anything more than a minor inconvenience to the estates involved because they can simply apply for individual licences to continue their game-shooting activities? We’ll have to wait and see.
RSPB Scotland’s response to the two General Licence Restriction orders here
As yet no response from Scottish Land & Estates or the Scottish Gamekeepers’ Association but we’ll post them here if/when they comment.
UPDATE 11.50hrs: The SGA has issued the following statement on their website:
On November 4th 2015, SNH announced general licence restrictions to two areas encompassing four properties.
The SGA has issued the following statement in response to questions.
A Spokesman for The Scottish Gamekeepers Association said: “The SGA cannot condone wildlife crime and has a clear and consistent policy regarding this.
“As regards this case, it is our understanding that legal discussions are taking place regarding the areas affected and, therefore, it is not appropriate for us to comment further.”
END
UPDATE 13.20hrs: Statement from Environment Minister Dr Aileen McLeod:
“The announcement by SNH that the use of general licences has been restricted on specified areas of land in the Borders and in Stirlingshire is a result of work that the Scottish Government commissioned in July 2013 as part of a package of measures to combat wildlife crime.
We welcome the progress that has been made with this work. However we have not been involved in the decision-making and do not have any comment on the individual cases in question. The General Licence system is a light touch form of regulation. It is clearly sensible to apply closer scrutiny to areas where there is good evidence that wildlife crime has taken place, and we believe that this will prove a useful tool in the fight against bird of prey persecution.”
 Further to last week’s news that SNH has suspended the use of General Licences on four estates for what it said was “clear evidence that wildlife crimes have been committed on these properties”, which includes the discovery of poisoned raptors and illegal traps (see here and here), two of the estates involved are set to appeal.
Further to last week’s news that SNH has suspended the use of General Licences on four estates for what it said was “clear evidence that wildlife crimes have been committed on these properties”, which includes the discovery of poisoned raptors and illegal traps (see here and here), two of the estates involved are set to appeal.
 Last week we blogged about the implementation of General Licence restrictions on parts of four properties: Burnfoot Estate & Wester Cringate Estate in Stirlingshire, and Raeshaw Estate & Corsehope Estate in the Borders (see
Last week we blogged about the implementation of General Licence restrictions on parts of four properties: Burnfoot Estate & Wester Cringate Estate in Stirlingshire, and Raeshaw Estate & Corsehope Estate in the Borders (see  West Mercia Police have issued an appeal for information following the discovery of a poisoned peregrine.
West Mercia Police have issued an appeal for information following the discovery of a poisoned peregrine.





 A year ago, gamekeeper Allen Lambert was convicted of a series of wildlife crime offences on the Stody Estate in Norfolk, including the mass poisoning of birds of prey (10 buzzards and one sparrowhawk) which had been found dead on the estate in April 2013 (see
A year ago, gamekeeper Allen Lambert was convicted of a series of wildlife crime offences on the Stody Estate in Norfolk, including the mass poisoning of birds of prey (10 buzzards and one sparrowhawk) which had been found dead on the estate in April 2013 (see  As part of the
As part of the 
 Yesterday the Scottish Government published its latest report on wildlife crime: ‘Wildlife Crime in Scotland: 2014 annual report’ (see
Yesterday the Scottish Government published its latest report on wildlife crime: ‘Wildlife Crime in Scotland: 2014 annual report’ (see