In April 2012, we wrote an article called ’21 eagles, 6 years, 0 prosecutions’ (see here).
In September 2012, we updated it and called it ’26 eagles, 6 years, 0 prosecutions’ (see here).
In July 2013 we updated it again. This time, ’27 eagles, 7 years, 0 prosecutions’ (see here).
In December 2013 we had to do another update: ‘31 eagles, 7 years, 0 prosecutions’ (see here).
In April 2014 we had to do another update: ’32 eagles, 8 years, 0 prosecutions’ (see here).
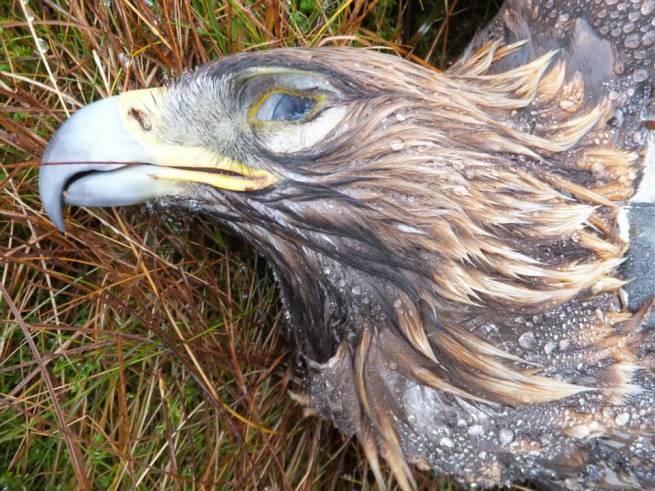

After this morning’s news (here) that eight young satellite-tagged golden eagles have ‘disappeared’ on grouse moors in the Monadhliath Mountains over the last five years, we thought it was time for another update. This time it’s called: ’40 eagles, 10 years, 0 prosecutions’.
36 of these 40 eagles have either been found dead on, or have ‘disappeared’ on, Scottish grouse moors. (The other 4 have either died or have ‘disappeared’ in other habitat types).
Three of these 40 eagles have ‘disappeared’ in 2016. So much for the grouse-shooting industry claiming that they’ve cleaned up their act and that persecution is a thing of the past. The tactics of how to kill an eagle have clearly changed (see here) but the persecution continues.
As before, a number of eagles included in this list (16 of them, to be precise) may not be dead. However, they are included here because their satellite tags unexpectedly stopped functioning (i.e. they’d been transmitting perfectly well up until the eagles’ last known location, often a known persecution hotspot). Two further satellite-tagged eagles (‘Angus’ and ‘Tom’) are not included in this list as although their transmitters stopped functioning, there had been recognisable problems with their tags prior to the final transmissions and so the benefit of the doubt has been applied.
Many of these listed eagles from recent years have only been discovered because the eagles were being satellite-tracked. Much kudos to the dedicated teams of fieldworkers who have put in hours and hours of skilled hard work to allow this to happen. Obviously there are many other eagles out there that have not been sat-tagged and on the balance of probability will have been killed at the hands of the game-shooting industry. 40 eagles in the last 10 years is the bare minimum. The number of prosecutions (zero) is indisputable.
MAY 2006: A dead adult golden eagle was found on the Dinnet & Kinord Estate, near Ballater, Aberdeenshire. Tests revealed it had been poisoned by the illegal pesticide Carbofuran. Grampian Police launched an investigation. No prosecution.
JUNE 2006: A dead golden eagle was found on Glen Feshie Estate in the Cairngorms. Tests revealed it had been poisoned by the illegal pesticide Carbofuran. Northern Constabulary launched an investigation. No prosecution.
AUGUST 2007: A dead adult female golden eagle was found on an estate near Peebles in the Borders. She was half of the last known breeding pair of golden eagles in the region. Tests revealed she had been poisoned by the illegal pesticide Carbofuran. Lothian & Borders Police launched an investigation. No prosecution.
NOVEMBER 2007: Tayside Police received a detailed tip-off that a young male white-tailed eagle (known as ‘Bird N’) had allegedly been shot on a grouse moor estate in the Angus Glens. The timing and location included in the tip-off coincided with the timing and location of the last-known radio signal of this bird. The eagle has not been seen again. With no carcass, an investigation isn’t possible.
MAY 2008: A one year old male white-tailed eagle hatched on Mull in 2007 and known as ‘White G’ was found dead on the Glenquoich Estate in the Angus Glens. Tests revealed he had been poisoned by an unusual concoction of pesticides that included Carbofuran, Bendiocarb and Isofenphos. A police search in the area also revealed a poisoned buzzard, a baited mountain hare and 32 pieces of poisoned venison baits placed on top of fence posts on the neighbouring Glenogil Estate. Laboratory tests revealed the baited mountain hare and the 32 poisoned venison baits contained the same unusual concoction of highly toxic chemicals that had killed the white-tailed eagle, ‘White G’. No prosecution.
JUNE 2009: An adult golden eagle was found dead at Glen Orchy, Argyll, close to the West Highland Way. Tests revealed it had been poisoned by the illegal pesticide Carbofuran. Strathclyde Police launched a multi-agency investigation. Three years and 3 months later, estate employee Tom McKellar pled guilty to possession of Carbofuran stored in premises at Auch Estate, Bridge of Orchy and he was fined £1,200. No prosecution for poisoning the golden eagle.
JULY 2009: A two year old female golden eagle known as ‘Alma’ was found dead on the Millden Estate in the Angus Glens. Tests revealed she had been poisoned by the illegal pesticide Carbofuran. Alma was a well-known eagle – born on the Glen Feshie Estate in 2007, she was being satellite-tracked and her movements followed by the general public on the internet. Tayside Police launched an investigation. No prosecution.
AUGUST 2009: A young white-tailed eagle was found dead on Glenogil Estate in the Angus Glens. Tests revealed it had been poisoned by the illegal pesticide Carbofuran. Tayside Police was criticized in the national press for not releasing a press statement about this incident until January 2010. No prosecution.
MAY 2010: #1 of three dead golden eagles found on or close to Skibo Estate, Sutherland. Tests revealed they had been poisoned; two with Carbofuran and one with Aldicarb. Northern Constabulary launched a multi-agency investigation. One year later (May 2011), Sporting Manager Dean Barr pled guilty to possession of 10.5 kg of Carbofuran stored in premises at Skibo Estate. No prosecution for poisoning the golden eagle.
MAY 2010: #2 of three dead golden eagles found on or close to Skibo Estate, Sutherland. Tests revealed they had been poisoned; two with Carbofuran and one with Aldicarb. Northern Constabulary launched a multi-agency investigation. One year later (May 2011), Sporting Manager Dean Barr pled guilty to possession of 10.5 kg of Carbofuran stored in premises at Skibo Estate. No prosecution for poisoning the golden eagle.
MAY 2010: #3 of three dead golden eagles found on or close to Skibo Estate, Sutherland. Tests revealed they had been poisoned; two with Carbofuran and one with Aldicarb. Northern Constabulary launched a multi-agency investigation. One year later (May 2011), Sporting Manager Dean Barr pled guilty to possession of 10.5 kg of Carbofuran stored in premises at Skibo Estate. No prosecution for poisoning the golden eagle.
JUNE 2010: #1: Leg rings with unique identification numbers that had previously been fitted to the legs of four young golden eagles in nests across Scotland were found in the possession of gamekeeper James Rolfe, during a multi-agency investigation into alleged raptor persecution at Moy Estate, near Inverness. It is not clear how he came to be in possession of the rings. The bodies of the eagles from which the rings had been removed were not found. No further action was taken in relation to the discovery.
JUNE 2010: #2: Leg rings with unique identification numbers that had previously been fitted to the legs of four young golden eagles in nests across Scotland were found in the possession of gamekeeper James Rolfe, during a multi-agency investigation into alleged raptor persecution at Moy Estate, near Inverness. It is not clear how he came to be in possession of the rings. The bodies of the eagles from which the rings had been removed were not found. No further action was taken in relation to the discovery.
JUNE 2010: #3: Leg rings with unique identification numbers that had previously been fitted to the legs of four young golden eagles in nests across Scotland were found in the possession of gamekeeper James Rolfe, during a multi-agency investigation into alleged raptor persecution at Moy Estate, near Inverness. It is not clear how he came to be in possession of the rings. The bodies of the eagles from which the rings had been removed were not found. No further action was taken in relation to the discovery.
JUNE 2010: #4: Leg rings with unique identification numbers that had previously been fitted to the legs of four young golden eagles in nests across Scotland were found in the possession of gamekeeper James Rolfe, during a multi-agency investigation into alleged raptor persecution at Moy Estate, near Inverness. It is not clear how he came to be in possession of the rings. The bodies of the eagles from which the rings had been removed were not found. No further action was taken in relation to the discovery.
JUNE 2010: A golden eagle was found dead on Farr & Kyllachy Estate, Inverness-shire. Tests revealed it had been poisoned by the illegal pesticide Carbofuran. Northern Constabulary apparently did not search the property until July 2011. No prosecution.
JUNE 2010: A white-tailed eagle was found dead on Farr & Kyllachy Estate, Inverness-shire. Tests revealed it had been poisoned by the illegal pesticide Carbofuran. Northern Constabulary apparently did not search the property until July 2011. No prosecution.
DECEMBER 2010: A decomposing carcass of a white-tailed eagle was found and photographed on Logie (Lochindorb) Estate, Morayshire. It was reported to Northern Constabulary. By the time the police arrived to collect it, the carcass had disappeared. The police said they couldn’t investigate further without the body.
FEBRUARY 2011: The signal from a young satellite-tracked golden eagle ( ‘Lee’, hatched in 2010) unexpectedly stopped transmitting after a final signal from the North Angus Glens. A technical malfunction or another mysterious ‘disappearance’?
MARCH 2011: The body of a young golden eagle was discovered on North Glenbuchat Estate, Aberdeenshire. Tests revealed it had been poisoned by the illegal pesticide Carbofuran. Grampian Police launched an investigation and raided the property in May 2011. A poisoned buzzard, a poisoned bait and a shot short-eared owl were found. No prosecution.
APRIL 2011: The body of a white-tailed eagle was found at the base of cliffs on Skye. The person who discovered it (a professional medic) considered it to have been freshly shot with a rifle, decapitated with a sharp implement and thrown from the cliff top. He took photographs and alerted Northern Constabulary and RSPB. There was a delay of two weeks before the now probably decomposed carcass was collected. A post-mortem was inconclusive. This incident was not made public until one year later after a tip off to this blog. No prosecution.
SEPTEMBER 2011: The signal from a satellite-tracked young golden eagle (‘Strathy’, hatched in 2010) unexpectedly stopped transmitting after a final signal from an Aberdeenshire grouse moor. A technical malfunction or another mysterious ‘disappearance’?
NOVEMBER 2011: The signal from a one-year-old satellite-tracked golden eagle (#57124) unexpectedly stopped transmitting after a final signal from a grouse moor in the Monadhliaths. A technical malfunction or another mysterious ‘disappearance’?
MARCH 2012: The body of a young golden eagle being tracked by satellite was discovered in Lochaber. Tests revealed it had been poisoned with the banned pesticides Aldicarb and Bendiocarb. Information about this incident was not made public until three months later. No prosecution.
MARCH 2012: The signal from a satellite-tracked young golden eagle (‘Angus 26′, hatched in 2011) unexpectedly stopped transmitting after a final signal from a grouse moor in the Angus Glens. This bird’s suspiciously damaged sat tag was found in the area. No prosecution.
MAY 2012: The signal from a young satellite-tracked golden eagle (#32857) unexpectedly stopped transmitting when the bird was north-east of the Cairngorms National Park. A technical malfunction or another mysterious ‘disappearance’?
MAY 2012: The dead body of a young satellite-tracked golden eagle (hatched in 2011) was discovered near a lay-by in Aboyne, Aberdeenshire. The data from its satellite tag & the injuries the bird had when found (2 broken legs) suggested it had been caught in an illegal trap on a grouse moor in the Angus Glens and then removed, under cover of darkness, to be dumped in another area where it was left to die, probably a slow and agonising death. Information on this incident was not released until almost five months later, by the RSPB. It appears the police failed to properly investigate this incident as we understand that no search warrants were issued and no vehicles were searched. No prosecution.
JULY 2012: The signal from a one-year-old satellite-tracked golden eagle (‘Foinaven’) unexpectedly stopped transmitting after a final signal from a grouse moor in the Monadhliaths. A technical malfunction or another mysterious ‘disappearance’?
OCTOBER 2012: An adult golden eagle was found shot and critically injured on grouse moor at Buccleuch Estate, near Wanlockhead, South Lanarkshire. The bird was rescued by the SSPCA and underwent surgery but it eventually succumbed to its injuries in April 2013. No prosecution.
MAY 2013: The signal from a two-year-old satellite tracked golden eagle (‘Angus 33′, hatched in 2011) unexpectedly stopped transmitting after its last signal from North Glenbuchat Estate in Aberdeenshire. A technical malfunction or another mysterious ‘disappearance’?
JUNE 2013: A dead golden eagle was found under power lines on an RSPB reserve on Oronsay. This bird had been shot although it is not known whether this was the cause of death or an historical injury.
JULY 2013: The signal from a young satellite tracked golden eagle (‘Cullen’, hatched 2010) unexpectedly stopped transmitting after its last signal in Aberdeenshire. A technical malfunction or another mysterious ‘disappearance’?
DECEMBER 2013: A two year old satellite tracked golden eagle (‘Fearnan’) was found dead on a grouse moor in the Angus Glens. Tests revealed he had been poisoned with the banned pesticide Carbofuran. No prosecution.
MARCH 2014: The signal from a one-year-old satellite-tagged golden eagle (#129002) unexpectedly stopped transmitting after a final signal from a grouse moor in the Monadhliaths. A technical malfunction or another mysterious ‘disappearance’?
APRIL 2014: The signal from a young satellite tracked white-tailed eagle (the first fledged sea eagle chick in East Scotland in ~200 years) unexpectedly stopped transmitting after its last signal from the North Glenbuchat Estate in Aberdeenshire. Police raided the property a couple of weeks later. No prosecution.
OCTOBER 2014: The signal from a one-year-old satellite-tagged golden eagle (#107133) unexpectedly stopped transmitting after a final signal from a grouse moor in the Monadhliaths. A technical malfunction or another mysterious ‘disappearance’?
OCTOBER 2014: The signal from a two-year-old satellite-tagged golden eagle (#119886) unexpectedly stopped transmitting after a final signal from a grouse moor in the Monadhliaths. A technical malfunction or another mysterious ‘disappearance’?
MAY 2016: The signal from a less-than-one-year-old satellite-tagged golden eagle (#00000583) unexpectedly stopped transmitting after a final signal from a grouse moor in the Monadhliaths. A technical malfunction or another mysterious ‘disappearance’?
JUNE 2016: The signal from a two-year-old satellite-tagged golden eagle (#129010) unexpectedly stopped transmitting after a final signal from a grouse moor in the Monadhliaths. A technical malfunction or another mysterious ‘disappearance’?
JULY 2016: The signal from a two-year-old satellite-tagged golden eagle (#129015 ‘Brodie’) unexpectedly stopped transmitting after a final signal from a grouse moor in the Monadhliaths. A technical malfunction or another mysterious ‘disappearance’?
THE UNTOUCHABLES: 40; JUSTICE: 0
Cabinet Secretary for the Environment Roseanna Cunningham has responded to this morning’s news (read her statement here) by calling for an analysis of the satellite tag data from around 90 surviving and missing eagles “to discover if there is a pattern of suspicious activity“. It just beggars belief. We’ll shortly be blogging in more detail about her response and that of the Scottish Moorland Group, which is equally as fatuous.
In the meantime, please sign this petition (here) calling on the Scottish Government to introduce a licensing scheme for gamebird shooting.
And then please sign this petition (here) calling on the Westminster Government to ban driven grouse shooting.















 Grant Moir, Chief Executive of the Cairngorms National Park Authority, has today issued a
Grant Moir, Chief Executive of the Cairngorms National Park Authority, has today issued a  Tim (
Tim (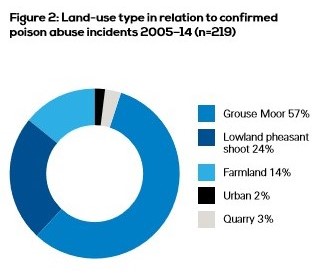
 Yesterday the RSPB published its latest figures on illegal raptor persecution in Scotland.
Yesterday the RSPB published its latest figures on illegal raptor persecution in Scotland.

 The season of mince pies may be upon us but the SGA is feasting on a hefty pile of pork pies.
The season of mince pies may be upon us but the SGA is feasting on a hefty pile of pork pies. As part of the
As part of the 