BREAKING NEWS!
The Scottish Government has finally published its response to the recommendations made in its commissioned review of increasing investigatory powers for the Scottish SPCA to help tackle wildlife crime, including raptor persecution. It’s good news!
Here’s the Government statement:
Scottish Government Response to Taskforce Report on SSPCA Powers
In response to the independent Scottish Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals (SSPCA) Taskforce report, the Scottish Government is proposing to bring forward provisions to allow for a limited extension of the Scottish SPCA’s current powers to investigate wildlife crime.
We are grateful to the SSPCA Taskforce for conducting the review and producing their final report and we agree with the recommendation that further partnership working between the SSPCA and Police Scotland should be taken forward. Having considered the report in detail, we also propose that further limited powers for SSPCA inspectors should be provided.
Our proposal is to provide SSPCA inspectors with additional powers to search, examine and seize evidence in connection with specified wildlife crime offences under Part 1 of the Wildlife and Countryside Act 1981 and certain offences in the Wildlife Management and Muirburn (Scotland) Bill 2023. These powers would only be given to an inspector appointed under section 49(2)(a) of the Animal Health and Welfare (Scotland) Act 2006 and each inspector would be separately and individually authorised by the Scottish Government in connection with the new powers. All inspectors would be required to undertake specified training prior to being given authorisation to exercise the new powers. Authorisations could be withdrawn at the discretion of the Scottish Government.
In addition to the additional training requirements, protocols will be established between the SSPCA and Police Scotland to ensure effective partnership working and that Police Scotland have primacy over cases and offences under the Wildlife and Countryside Act 1981 and the Wildlife Management and Muirburn (Scotland) Bill 2023.
It is intended that an important limitation would be placed on the exercise of these powers, namely that the additional powers could only be exercised when an inspector is already responding to a case using their existing powers under the 2006 Act.
This has been a long-running issue and we believe that the approach we are proposing represents a balanced compromise. It will allow SSPCA inspectors who are already on the spot, investigating potential animal welfare offences under their existing powers, to seize and secure evidence of related wildlife crimes without delay and potential loss of that evidence. The proposal would not however lead to SSPCA becoming an alternative wildlife crime enforcement agency. Police Scotland would retain primacy as the enforcement body for all wildlife crime and the public should continue to report those crimes to Police Scotland.
Following further consultation with stakeholders the proposed changes will be brought forward as an amendment at Stage 2 of the Wildlife Management and Muirburn (Scotland) Bill 2023. The Bill is currently before the Parliament and we welcome more evidence on this being provided at Stage 1.
ENDS
This is a surprisingly good outcome, given where we were the last time the Government made a decision on the issue back in May 2017, when increased investigatory powers were ‘ruled out’, apparently ‘on legal advice’ (see here).
I don’t know what that ‘legal advice’ was in 2017 – my own view is that this was just a convenient excuse at the time, because the law hasn’t changed since then but now increased powers are suddenly possible? Hmm.
The proposed new powers are limited, yes, but they’re a good starting point.
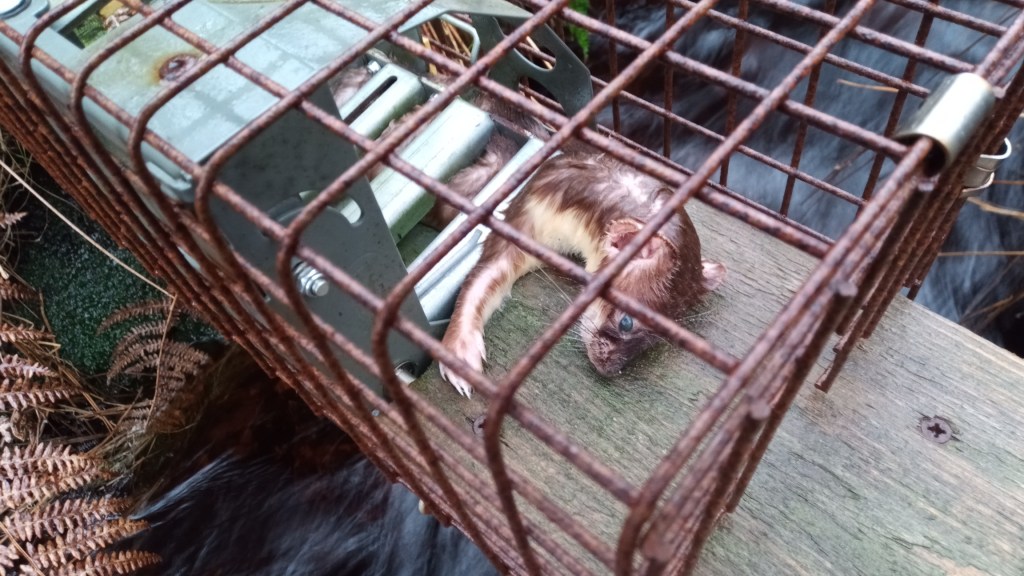
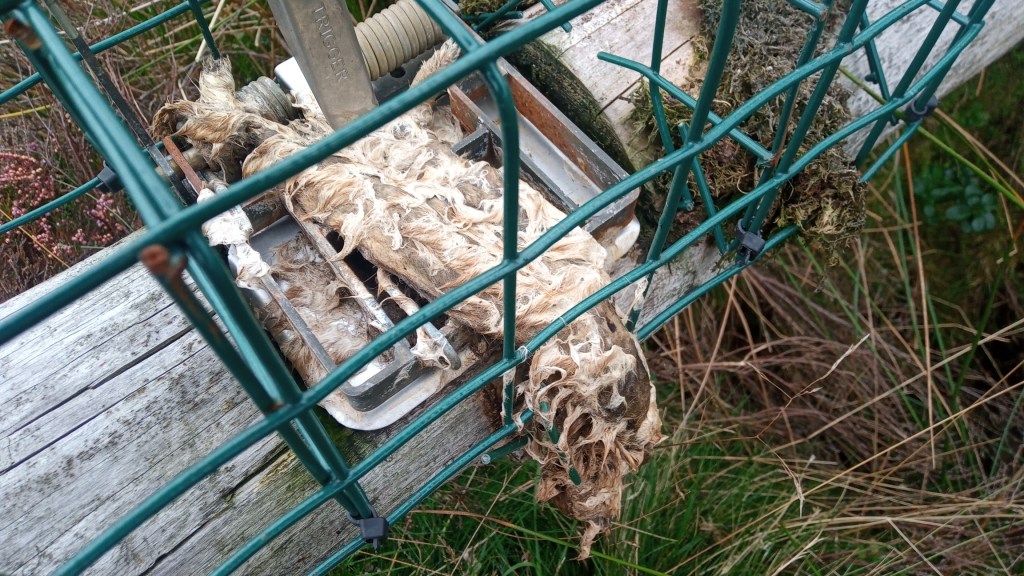
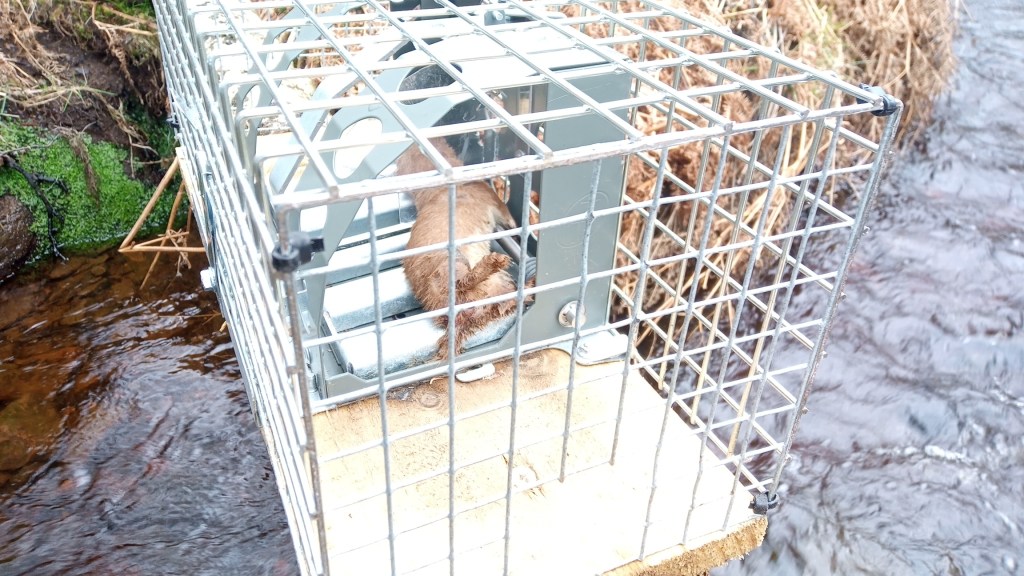
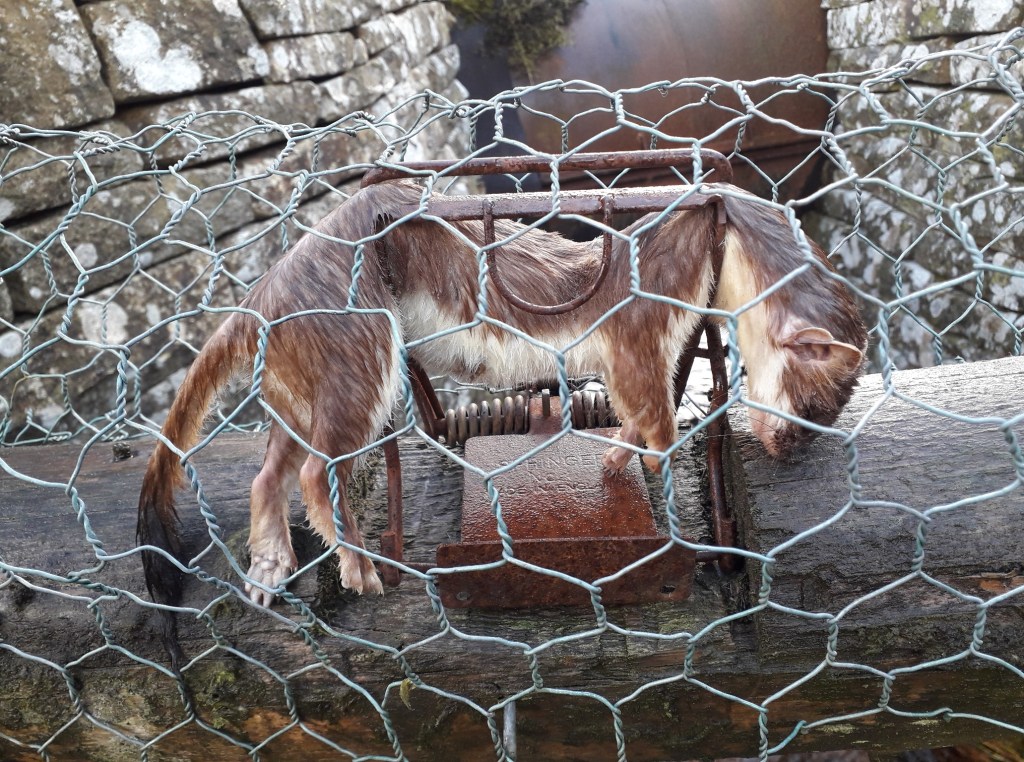
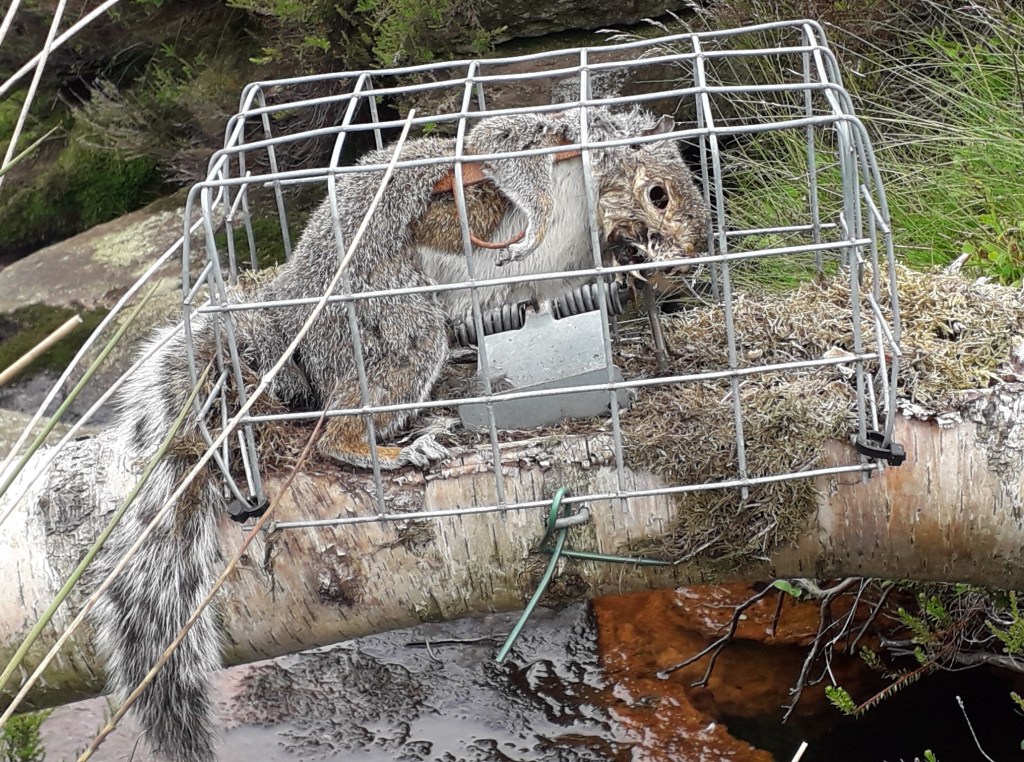
Had these powers been in place previously then I dare say we might have seen a better outcome in a number of wildlife crime cases where the SSPCA were already on scene investigating alleged animal welfare offences but were not permitted to collect evidence of further wildlife crimes that were staring them in the face – e.g. the illegally-set spring traps on a grouse moor on the Invercauld Estate in the Cairngorms National Park (see here) and the carcasses of nine shot raptors found in bags in and around the grouse moors of Millden Estate in the Angus Glens (see here).
I’m not sure whether the Scottish Government is proposing yet another consultation on this issue (‘Following further consultation with stakeholders the proposed changes will be brought forward as an amendment at Stage 2 of the Wildlife Management and Muirburn (Scotland) Bill 2023‘) – surely to God we don’t need another bloody consultation – I’ve lost track of the number of consultations on this issue – we know where every organisation stands and none of them have changed their minds, or are likely to do so now. The general position is that the game shooting lobby don’t want the SSPCA to have increased investigatory powers (gosh, can’t think why) and the conservation organisations do want them to have increased powers.
Let’s see what happens between now and Stage 2 of the Wildlife and Muirburn (Scotland) Bill when the Government’s proposals will be debated. Stage 2 is expected to begin in the autumn.
For now, well done and thanks to everyone who has campaigned on this issue for the last 13 years, and thanks especially to Mark Ruskell MSP (Scottish Greens) who has championed the cause for many years.
This is not everything we wanted but nevertheless it’s a big win.
UPDATE 21.30hrs: Reaction to proposed new investigatory powers for Scottish SPCA to help tackle wildlife crime (here)