Anyone who has been reading the ‘official’ annual raptor persecution reports over the last few decades will be familiar with the phrase, “These figures represent the tip of the iceberg”. Conservationists have long held the view that many illegal raptor persecution incidents go unreported, given the remote locations involved and the cultural and social pressures that inhibit certain sectors of the rural community from speaking up about these crimes. Most reports of poisoned, shot, or trapped raptors come from people who have found them by chance, for example hill walkers and dog walkers. The game shooting lobby, in response to the ‘tip of the iceberg’ statement, usually asks, “Where’s the evidence?” The numerous (and ever-increasing) glut of peer-reviewed scientific publications, that show a clear correlation between persecution and upland grouse moors, are usually dismissed as ‘pseudo-science’ by the landowners and gamekeepers, and the conservationists are often accused of conducting some sort of smear campaign against the game shooting industry.
No doubt we will hear all of this, and more, in the coming few days once the RSPB Birdcrime 2010 report has been published later this week. For certain, the report will contain the statement, “These figures represent the tip of the iceberg”, or words to that effect.
So, if the gamekeepers want evidence, here’s some that was unwittingly provided by….er, gamekeepers. It comes in the form of a recently (Sept 2011) published paper in the journal Scottish Birds, which is published by the Scottish Ornithologists’ Club. The paper was written by R.L. McMillan and is entitled, ‘Raptor persecution on a large Perthshire estate: a historical study’. Unfortunately we’re not allowed to publish the whole paper here (you have to be a member of the SOC to get access, or google the author and ask him for a PDF for your personal use) but here is the abstract:
The Atholl Game and Vermin Lists provide an almost continuous record from 1867 until 1988 and in many respects are unique for a large estate in Scotland. Large numbers of raptors and owls were destroyed by gamekeepers during the latter part of the 19th century and into the late 20th century. The implementation of legislation to protect predatory birds appears to have made little difference to persecution levels. Gamekeepers on individual beats seemed able to decide whether they killed predators or not. A few gamekeepers chose not to kill any birds of prey. Some persecution continued well into the late 20th century and a comparison between estate records and incidents recorded by the authorities strongly suggests that a substantial amount of illegal persecution was not recorded.
The paper provides a detailed insight into the extent of raptor persecution on Atholl Estate, covering the historical period when it was legal to kill raptors (pre-1954), and the current period when it is illegal to kill raptors (1954 onwards). Gamekeepers on the nine beats at Atholl Estate were required to submit annual report cards that recorded the number of game and ‘vermin’ [including raptors!] that was killed on each beat. According to the paper, McMillan writes of Atholl Estate:
“To maintain the estate record of game and vermin killed, the individual shooting beats were required to complete a card by the end of February each year and this contained details from the preceding year. The same printed card had been in use for many years and this included hawks, owls and ravens. Although the estate factor regularly checked the returns on these cards, it was only when a member of staff expressed concern that protected birds were included in the returns, that a new form was introduced for the 1988/89 season which excluded protected species”.
The historical records covering part of the period (1867-1911) when it was legal to kill raptors don’t provide any surprises, showing that 11,428 ‘hawks’ were killed on Atholl Estate, in addition to 3,731 owls. Sadly the records do not distinguish between different species of ‘hawks’ or owls and McMillan has interpreted the term to include every raptor and owl species that would typically occur in the area.
The more recent records, however, are of far more interest. They show the period covering the introduction of the 1954 Protection of Birds Act (making it illegal to kill all raptors except sparrowhawks, which weren’t protected until 1961) and McMillan’s graphs of persecution incidents show that the legislation was ignored on the two beats whose records he analysed. In fact on one beat, McMillan shows that persecution actually increased at the time the Act was implemented.
But the most interesting part of this paper comes in Table 3. It is a comparison of gamekeeper records from just one Atholl Estate beat, with the ‘official’ RSPB data for the whole of Scotland, from the period 1980 – 1988. The RSPB data only include details of raptors that have been killed (so not details of ‘suspected’ incidents). Here’s an overview of McMillan’s findings:
1980/81: Atholl Estate beat = 19 raptors killed; RSPB official data for all of Scotland= 9 raptors killed.
1981/82: AE beat = 21; RSPB all Scotland= 23.
1982/83: AE beat = 36; RSPB all Scotland= 16.
1983/84: AE beat = 36; RSPB all Scotland = 13.
1984/85: AE beat = 25; RSPB all Scotland= 12.
1985/86: AE beat = 22; RSPB all Scotland= 8.
1986/87: AE beat = 14; RSPB all Scotland= 13.
1987/88: AE beat = 30; RSPB all Scotland = 15.
So, in each of the years listed, with the exception of 1981/82, the ‘official’ RSPB figures for the WHOLE of Scotland were lower than the number of illegally persecuted raptors on just one shooting beat. Does anyone need any clearer evidence that the ‘official’ statistics of illegal raptor persecution are just the tip of the iceberg?!! Of course, there are plenty of arguments that could be made about the reliability of the gamekeepers’ records – i.e. keepers could have inflated the number to earn a bonus, or alternatively keepers could have reduced the number for fear of providing potentially incriminating evidence. McMillan deals with these and other issues in the paper. And for those who think the persecution stopped when Atholl Estate stopped recording it in the 1988/89 season, McMillan reports that “between 1989 and 1999, a number of incidents were logged by the RSPB on several shooting beats on the Atholl Estates, not all of which were confirmed, but which included shootings of raptors, trapping of birds including golden eagle and the deliberate destruction of broods of hen harrier and peregrines“.
It’s worth bearing in mind that these figures in Table 3 are from just ONE beat on just ONE sporting estate. You don’t need much imagination to guess what these figures would look like if records from every sporting estate in Scotland were included in the analysis. This should provide some perspective when we read the ‘official’ figures in the RSPB Birdcrime 2010 report later this week.
It should be noted that under the current management, Atholl Estate regularly provides a home for breeding golden eagles, peregrines, hen harriers and other raptors.
Full paper citation: McMillan, R.L. (2011). Raptor persecution on a large Perthshire estate: a historical study. Scottish Birds 31(3): 195-205.
Atholl Estate website here
Thank you to the contributor who alerted us to this publication.

 An article on the STV website reports that a gamekeeper on the Aswanley Estate has lost his court appeal against his sentence for illegal possession and control of a wild bird.
An article on the STV website reports that a gamekeeper on the Aswanley Estate has lost his court appeal against his sentence for illegal possession and control of a wild bird.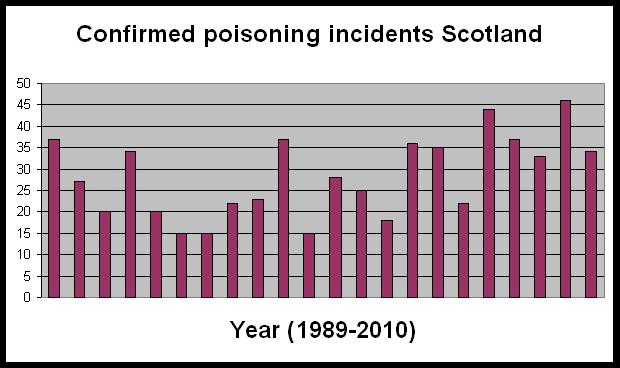 If you look closely at the graph, you will see a great deal of variation between years in the number of confirmed poisoning incidents. Of particular interest are the years 1994 and 1995 – in these two years, confirmed poisoning incidents dropped to a low of 15 from a previous high of 35+. However, if you then look at the following three years, the number of confirmed incidents steadily rose until they reached 35+ again. In 1999, the figure dropped again to 15, and from then until 2010, that figure has steadily risen and fallen, although never reaching the low of 15 again. So what does that tell us? I’m fairly sure that in the years 1994 and 1995, the game shooting lobby would have declared a ‘victory’ as the figures had dropped so much, and would have shouted from the hilltops that they’d changed their ways. I’m also fairly sure that in the following three years when the figures rose again, the conservationists would have declared a ‘victory’ and pronounced that their claims of widespread persecution had been vindicated. Either way, it is clear that neither ‘side’ can draw conclusions just based on an annual figure; for a trend to be detected, we need to see long-term figures.
If you look closely at the graph, you will see a great deal of variation between years in the number of confirmed poisoning incidents. Of particular interest are the years 1994 and 1995 – in these two years, confirmed poisoning incidents dropped to a low of 15 from a previous high of 35+. However, if you then look at the following three years, the number of confirmed incidents steadily rose until they reached 35+ again. In 1999, the figure dropped again to 15, and from then until 2010, that figure has steadily risen and fallen, although never reaching the low of 15 again. So what does that tell us? I’m fairly sure that in the years 1994 and 1995, the game shooting lobby would have declared a ‘victory’ as the figures had dropped so much, and would have shouted from the hilltops that they’d changed their ways. I’m also fairly sure that in the following three years when the figures rose again, the conservationists would have declared a ‘victory’ and pronounced that their claims of widespread persecution had been vindicated. Either way, it is clear that neither ‘side’ can draw conclusions just based on an annual figure; for a trend to be detected, we need to see long-term figures. You need to be a subscriber to the journal Biological Conservation to access the full paper (or alternatively you can buy it [see link at foot of this post] or you can google the paper’s lead author, Dr Arjun Amar, to see if he’ll send you a free PDF for your own private use), but here is the published abstract:
You need to be a subscriber to the journal Biological Conservation to access the full paper (or alternatively you can buy it [see link at foot of this post] or you can google the paper’s lead author, Dr Arjun Amar, to see if he’ll send you a free PDF for your own private use), but here is the published abstract: