 Yesterday the RSPB published its latest figures on illegal raptor persecution in Scotland.
Yesterday the RSPB published its latest figures on illegal raptor persecution in Scotland.
Rather than their usual annual review, this time they’ve produced a 20-year review covering the period 1994-2014. This is a really useful exercise as it puts the scale of (known) persecution in to perspective. It’s a sobering read.
A total of 779 birds of prey were confirmed to have been illegally killed during this period, either by poisoning, shooting or trapping. The known victims included 104 red kites, 37 golden eagles, 30 hen harriers, 16 goshawks, 10 white-tailed eagles and 458 buzzards.
In addition to these confirmed victims, a further 171 incidents are documented where poisoned baits and/or non-birds of prey victims were found, including 14 pet cats and 14 pet dogs, and then a further 134 incidents where no victim had been found but clear attempts to target raptors had been uncovered (e.g. illegally-set traps).
The report includes a map showing the landholdings of all known persecution incidents during this period. As ever, it’s pretty revealing, with a handful on the west coast but the vast majority in the uplands of central, eastern and southern Scotland – areas dominated by driven grouse shooting.

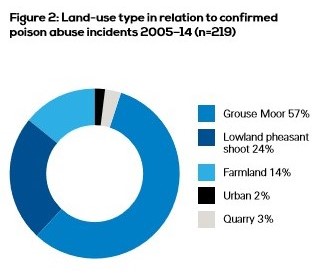
Drilling down in to the detail, there’s a useful analysis of land-use type of confirmed poisoning incidents between 2005-2014 (219 incidents). A shocking (or not) 81% of confirmed poisoning incidents during this nine-year period were on land used for game-shooting: 57% on grouse moors and 24% on land managed for lowland pheasant shoots. This tells us a great deal about who is responsible for the vast majority of illegal raptor poisoning. Despite their continued denials and protestations, and their increasingly-desperate attempts to minimise the scale of these crimes (“it’s just a few rogues”, “it’s just a small minority”), this graphic exposes the criminality at the heart of the game-shooting industry:
Further damning evidence, which isn’t needed by most of us but for the benefit of those who are still in denial of the bleedin’ obvious, is this graph showing the occupations of those convicted of raptor persecution between 1994-2014. Surprise, surprise, 86% of them were gamekeepers:

RSPB Scotland is to be commended for publishing this exceptionally detailed and meticulously-researched report. There are a number of things in it that are of particular interest to us and we’ll come back to those in due course. For now though, particular recognition should go to the Investigations team – they may be small in number but their contribution to exposing the disgraceful continuation of illegal raptor persecution in Scotland is enormous. They, and their colleagues south of the border, are worthy of high acclaim. If anybody reading this is in a position to recognise excellence in the field of raptor conservation, e.g. a nomination for an award, this team should be at the top of your list.
So, how has the Environment Minister, Dr Aileen McLeod, responded to such an embarrassing report? She said: “There is no doubt that the figures in this report make for uncomfortable reading, but we have made progress in recent years with the new vicarious liability provisions, the publication of the report from the Wildlife Crime Penalties Review Group, new measures implementing restrictions on the use of General Licences and earlier this year the Scottish Government funded pesticide disposal scheme that removed over 700kg of illegally held poisons in Scotland“.
“We have made progress…” Hmm. Let’s have a look:
Vicarious liability – introduced almost 4 years ago and only two successful convictions to date. A slow (but good) start, but we need to see many more convictions.
Wildlife Crime Penalties Review – Commissioned over two years ago, published last month. An excellent report calling for tougher sanctions but we’re waiting to hear whether the Environment Minister will act on the recommendations. Can only be defined as ‘progress’ if she agrees to act.
General Licence restrictions – available to be used against landholdings where raptor crimes committed/suspected from 1st January 2014. So far, only two restrictions have been implemented and those only lasted for six days each before they were suspended as legal arguments continue. A slow start, and the legal challenges were to be expected, but can’t be defined as ‘progress’ unless the restrictions are fully implemented. There should also be a lot more of them.
Pesticide disposal scheme – implemented this year and resulted in the removal of some illegally-held poisons. That is progress, although it is tinged with frustration that the game-shooting industry was given yet another chance to avoid justice as this scheme (the second of its kind) comes 14 years after the pesticides were originally banned. It’s also interesting to note in the RSPB’s report (page 18) that evidence suggests a number of individuals have retained their illegal stocks. This is supported by more poisoning incidents that have taken place this year, after the disposal scheme ended.
So some progress has been made (and almost entirely due to the efforts of Dr McLeod’s predecessor, Paul Wheelhouse) but it is glacially slow and, so far, has not stemmed the occurrence of illegal persecution, as the damning figures in this report show all too clearly. Much, much more can and needs to be done before we’ll be convinced that Dr McLeod is having any sort of impact. She has, though, announced that tenders have just been invited for a review of game licensing practices in other countries (to inform a possible decision of introducing licensing to game-shooting estates in Scotland), and that’s a good thing, but again, the research needs to be done and then a decision made, which probably won’t happen for a number of years if past performance is anything to go by. She’d find herself with a lot more support if she got on with announcing increased investigatory powers for the SSPCA – the public consultation closed 1 year and 3 months ago – and still we await her decision as the criminals continue their rampage. It’s not impressive at all.
And what of the response of the game-shooting industry itself? Some didn’t bother to publish a statement (Scottish Gamekeepers’ Association), which ironically tells us quite a lot, although they are quoted in an article by STV (see media coverage below) where they revert to type and simply deny the evidence and slag off the RSPB instead. And remember, the SGA is a fully-paid up member of the Partnership for Action Against Wildlife Crime (cough).
Scottish Land and Estates (SLE), another PAW partner, did manage to issue a statement, via their Scottish Moorland Group (see media coverage below). Again, it’s the usual lamentable denial, characterised beautifully by this statement from Director Tim (Kim) Baynes:
“Bird of prey deaths……have fallen dramatically over the last five years in particular“.
Er, here are some persecution figures that Kim might want to re-punch in to his calculator:
2012 – 18 confirmed deaths
2013 – 28 confirmed deaths
2014 – 37 confirmed deaths
There’s also this statement:
“Our condemnation of wildlife crime is unquivocal...” All very touching but how is that “condemnation” manifested in the real world? It’s been brought to our attention that the current head gamekeeper on a Scottish grouse shooting estate has a (spent) conviction for shooting dead a raptor when he worked on another Scottish grouse moor. How does a criminal with a conviction like that (spent or not) remain employed in the game-shooting industry, let alone get a senior position on another Scottish grouse moor? Was he one of the posse of moorland gamekeepers recently invited to Holyrood to mingle with, and be applauded by, a number of MSPs, as part of the Gift of Grouse propaganda campaign? Surely not…
Download the RSPB report here
Media coverage
RSPB press release here
Statement from Environment Minister Dr Aileen McLeod here
Scottish Moorland Group statement here
BBC news here
STV article here
BBC Radio Scotland (Newsdrive) interview with Ian Thomson, Head of Investigations RSPB Scotland here (starts at 21.50, available for 29 days)
Guardian article here (a mis-leading headline but nevertheless good to see coverage in this paper)









 So, it’s been two years since 22 dead birds of prey were discovered in a small area around Conon Bridge in the Highlands. It was one of the most significant illegal raptor persecution crimes ever uncovered in the UK.
So, it’s been two years since 22 dead birds of prey were discovered in a small area around Conon Bridge in the Highlands. It was one of the most significant illegal raptor persecution crimes ever uncovered in the UK. Regular blog readers will know we’ve been following the case of Scottish gamekeeper William Curr, who had been charged last year with alleged snaring offences on Glenogil Estate in the Angus Glens, said to have occurred in September 2014 (see
Regular blog readers will know we’ve been following the case of Scottish gamekeeper William Curr, who had been charged last year with alleged snaring offences on Glenogil Estate in the Angus Glens, said to have occurred in September 2014 (see 
 Back to the Rural Affairs, Climate Change & Environment (RACCE) committee meeting in January….
Back to the Rural Affairs, Climate Change & Environment (RACCE) committee meeting in January….

 Yesterday the RSPB published its latest figures on illegal raptor persecution in Scotland.
Yesterday the RSPB published its latest figures on illegal raptor persecution in Scotland.



