Today is the 26th November 2021. It’s been exactly one year since the then Environment Minister Mairi Gougeon announced the Scottish Government’s long-awaited response to the Werritty Review on grouse moor management and a decision to implement a licensing scheme for grouse shooting.
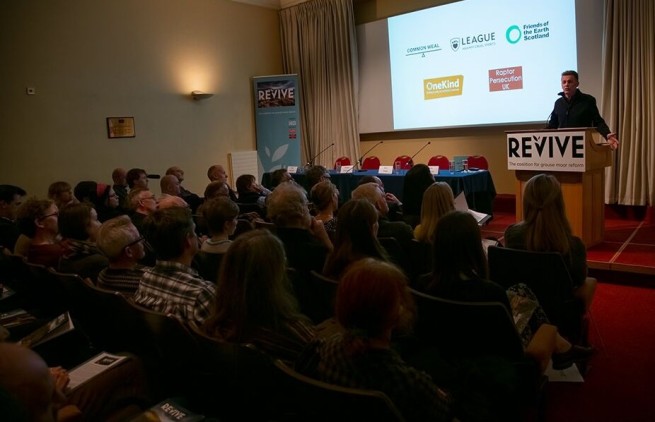
How we got to that position was the subject of a talk I presented at the REVIVE national conference a couple of weeks ago, hosted by Chris Packham at Perth Concert Hall.
[Chris Packham opening the REVIVE coalition for grouse moor reform conference. Photo by Ruth Tingay]

There had been an intention for a recording of the entire event to be made available but we learned subsequently that unfortunately the venue’s audio system had failed. REVIVE’s campaign manager, Max Wiszniewski has since published a conference overview (here) but I thought I’d take the opportunity to share the main points from my talk, to try and put Mairi Gougeon’s announcement in to some sort of context, and it seems fitting to do that today.
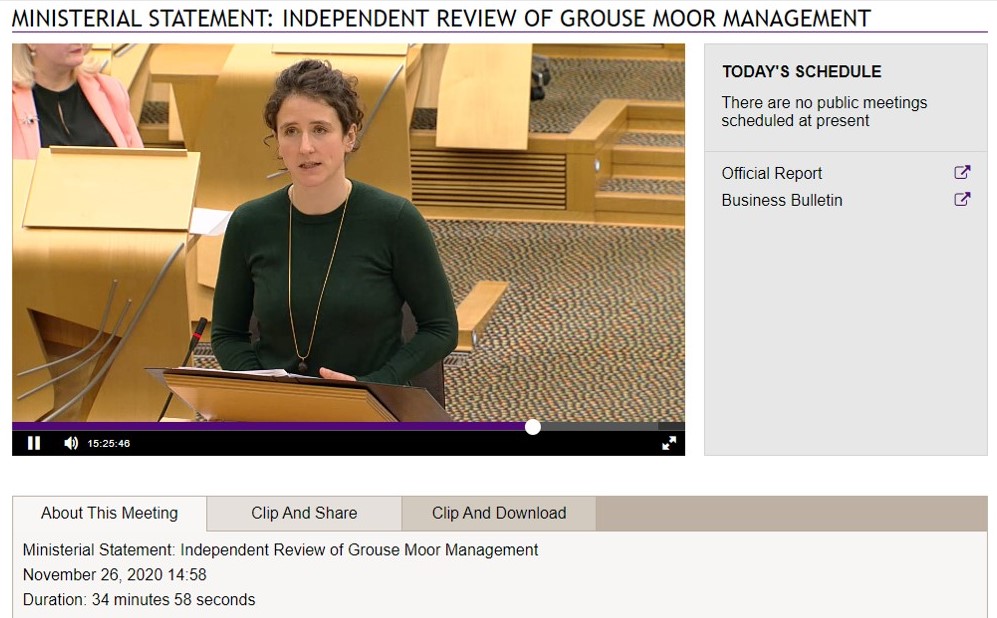
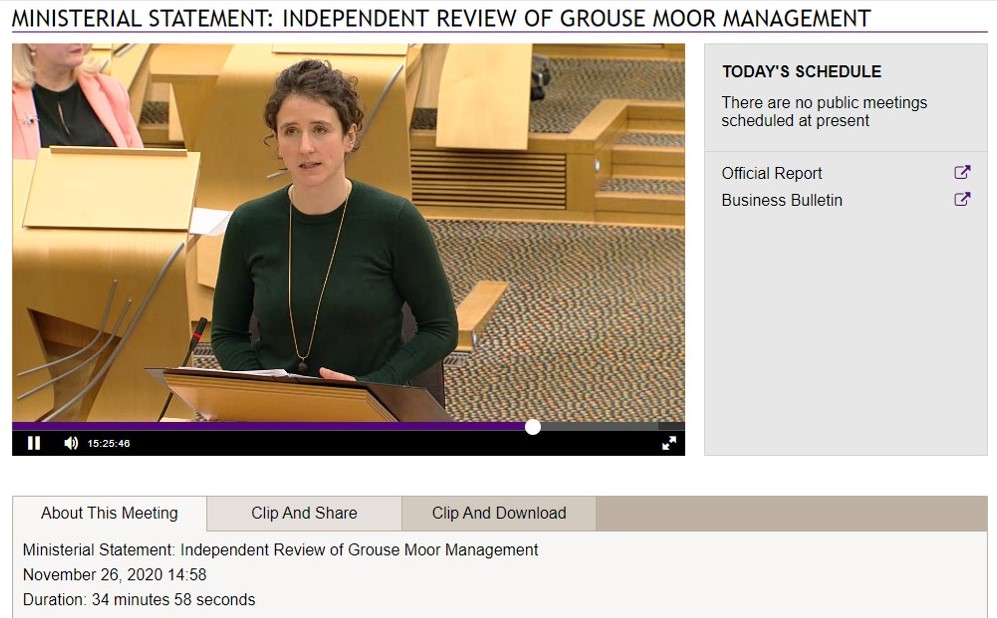
My opening slide was a screengrab of Minister Gougeon making that historic statement on 26th November 2020:
“The key recommendation put forward in the Werritty report – is that a ‘licensing scheme be introduced for the shooting of grouse’. This is a recommendation that I accept.
However, while I the understand why the review group also recommended that such a scheme should be introduced if, after five years, ‘there is no marked improvement in the ecological sustainability of grouse moor management’, I believe that the Government needs to act sooner than this and begin developing a licensing scheme now”.
There’s no question that this was a significant statement and although some campaigners were disappointingly dismissive (including several commentators on this blog), I think that when you understand the history of exactly what it took to get there, over many, many years of hard campaigning at substantial personal cost to many, you’ll hopefully appreciate why so many of us celebrated it as a huge victory. It’s not the end point, not by any means, but it is hugely symbolic of the direction of travel.
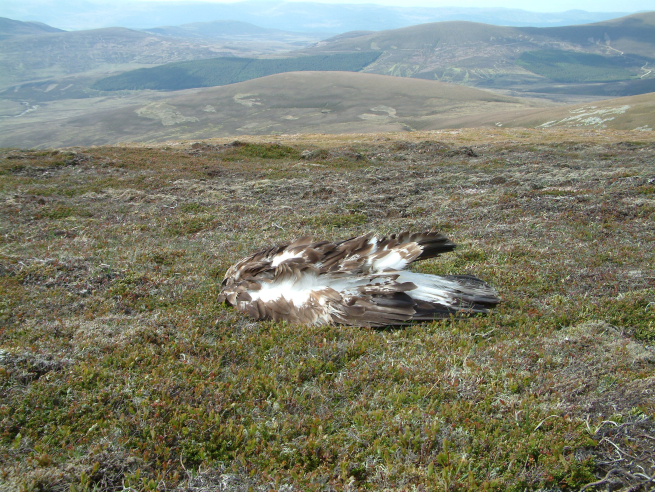
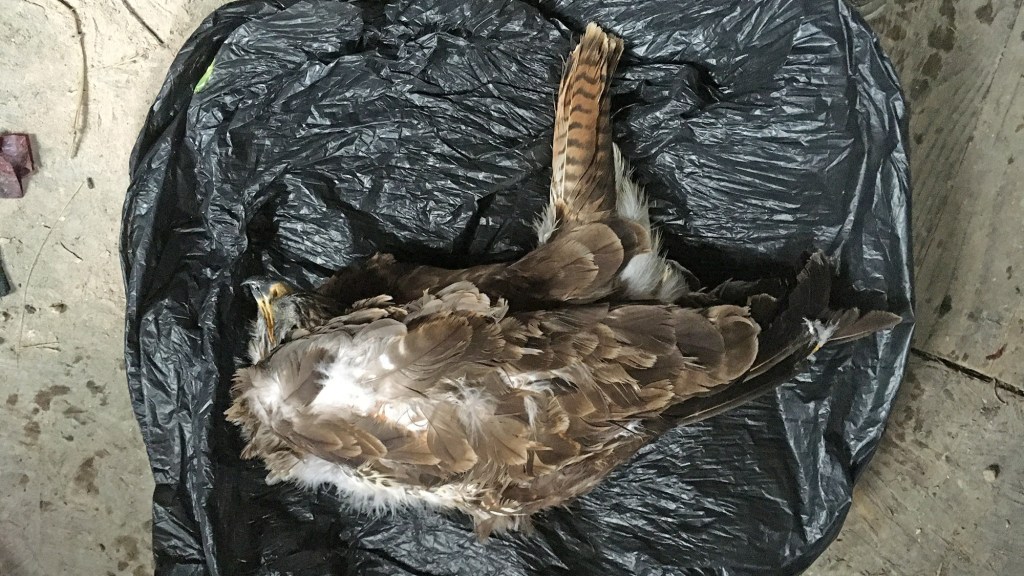
My next slide is a photo that I use in pretty much every talk I give on raptor persecution in the UK:
This is a photograph of a young golden eagle, found illegally poisoned on a grouse moor in the Cairngorms National Park in 2006. It was photographed by former RSPB Investigator Dave Dick (now retired) who had been sent out to retrieve it for post mortem. He had picked up many other illegally killed birds of prey on grouse moors over the years, but this image epitomises everything in its pitiful, poignant, senselessness.
I asked the audience to hold this image in their head as the talk progressed to cover some of the key moments in this long campaign against criminal activity and for effective law enforcement against those criminals.
I started with the basics – the 1954 Protection of Birds Act which brought legal protection for all raptor species in the UK, with the exception of the sparrowhawk which finally received full protection in 1961. So for most UK birds of prey, they’ve supposedly been protected for 67 years! This isn’t a new law that society needs time to adjust to and for which we should forgive any lack of adherence. This legislation was enacted a lifetime ago and was probably in place before every current working gamekeeper was even born. Ignorance of the law is no defence and that statement applies here, in spades.
In 1998, 44 years after raptors were declared ‘protected species’ in law, the then Secretary of State, Donald Dewar described the level of raptor persecution in Scotland as “a national disgrace“. He promised that following devolution the following year, the Scottish Government would take “all possible steps to eradicate it”.
RSPB Scotland started publishing annual reports in 1994, meticulously documenting raptor persecution. Their 20th report, published in 2004, documented that 779 birds of prey had been confirmed illegally killed between 1994 and 2004. This figure was considered the tip of the iceberg as wildlife crime, including raptor persecution, is widely recognised as being under-recorded for a number of reasons.
During the late 1990s-mid-2000s, and actually continuing to this day, researchers published a suite of scientific papers documenting the impact of illegal raptor persecution. This wasn’t just the odd ‘rogue incident’ here and there; raptor persecution was so extensive and systematic it was having population-level impacts on a number of species, notably the golden eagle, hen harrier, peregrine and red kite. The peer-reviewed evidence was conclusive – much of the killing was linked to game-shooting, and particularly to driven grouse moor management.
[An expanse of driven grouse moors inside the Cairngorms National Park. Photo by Ruth Tingay]
In 2000, the UK Raptor Working Group (established in 1995 and comprising a variety of statutory agencies, conservation NGOs and game-shooting bodies) published a report with a series of recommendations to address the recovery of bird of prey populations and their perceived impact on gamebirds, moorland management and pigeon racing.
In 2002, Scottish Natural Heritage (SNH) advised the Scottish Executive to accept most of the recommendations of the 2000 report and this led to many developments, with a particular focus on partnership working. Most of these so-called partnerships have since proven to be utterly ineffective (e.g. Partnership for Action Against Wildlife Crime Raptor Group, Heads Up for Hen Harriers) mostly due to them being heavily weighted towards game-shooting interests who seem intent on preventing progress by means of constant denial and obfuscation.
In 2004, raptor satellite-tagging began as a novel method of studying the biology and ecology of several species, notably the golden eagle. The significance of this will become apparent later.
[Two young golden eagles fitted with satellite tags prior to fledging. Photo by Dan Kitwood]
In 2005 the Possession of Pesticides (Scotland) Order was enacted, making it an offence for anyone to possess any of the eight highly toxic poisons used most frequently for killing birds of prey. This piece of legislation has proven useful in that it has allowed law enforcement agencies to prosecute for the lesser offence of ‘possession’ in cases where it has been virtually impossible to provide sufficient evidence to prosecute for actually poisoning a bird of prey.
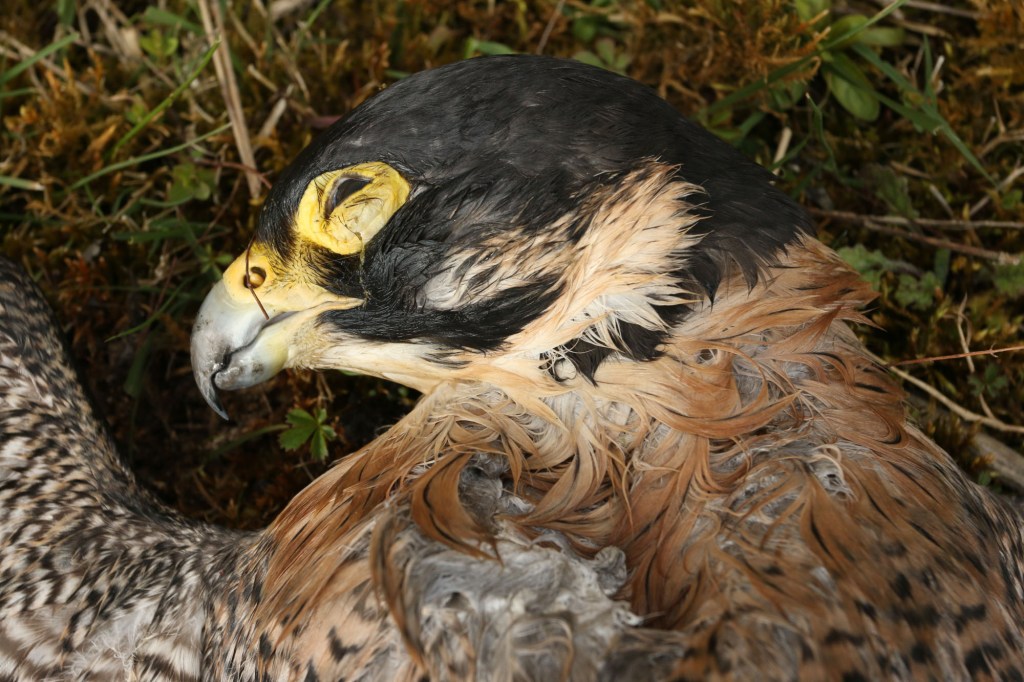
In 2007 an adult golden eagle was found poisoned at her nest site in the Borders. She was part of the only breeding pair in the region. Nobody was prosecuted and the ensuing public outrage resulted in the then Environment Minister Mike Russell ordering a Thematic Review into the prevention, investigation and prosecution of wildlife crime, which led to a series of recommendations to improve enforcement activities.
[Police officer Mark Rafferty holding the poisoned corpse of the Borders golden eagle. Photo by Dave Dick]
In 2010, this blog was launched primarily to raise public awareness about the scale of illegal raptor persecution in Scotland. It was later widened to cover the whole of the UK. It’s had over 7.5 million views to date.
In 2011, the Scottish Government launched a poisons disposal scheme, offering a sort of ‘amnesty’ and the safe destruction of any banned poisons that might have been left over from when it was legal for people to have these toxins in their possession (i.e. pre-2005).
Also in 2011, Peter Peacock MSP put forward an amendment for the Wildlife & Natural Environment (Scotland) Bill to introduce additional powers for the Scottish SPCA to enable them to investigate a wider suite of wildlife crime, including raptor persecution. Then Environment Minister Roseanna Cunningham rejected the amendment but committed to launch a public consultation on this subject.
Later in 2011 the Wildlife & Natural Environment (Scotland) Act was enacted and in 2012 this led to the Scottish Government having to publish its first annual wildlife crime report. The legislation also brought in vicarious liability, providing an opportunity for prosecutions against landowners and sporting agents whose employees had committed certain offences linked to raptor persecution. After almost ten years there have only been two successful prosecutions. That’s not because there haven’t been more opportunities for prosecution – there have been plenty – it’s because for the most part the Crown Office has refused to take the cases. When pushed for an explanation we’ve simply been told ‘it’s not in the public interest to proceed’. One case was not progressed because the landowner / hierarchy of supervision could not be established because the identity of the person was hidden in an offshore trust.
In 2013 the then Environment Minister Paul Wheelhouse ordered a review of the penalties available for wildlife crime and appointed Professor Poustie to lead the review.
Also in 2013, after RSPB video evidence was published showing a gamekeeper allegedly shooting a hen harrier on its nest on a grouse moor in Morayshire, which led to a prosecution that was later dropped because the Crown Office ruled the evidence ‘inadmissible’, huge public uproar led to Environment Minister Paul Wheelhouse having discussions with the Lord Advocate about maximising opportunities for prosecution and the Lord Advocate subsequently instructed the Crown Office to utilise all investigative tools for enforcement against wildlife crime. This had zero impact – several other high profile cases involving RSPB video evidence have also since been dropped due to this apparent inadmissibility.
[A screen grab from an RSPB video showing the alleged shooting of a hen harrier on a grouse moor]
In 2014 Environment Minister Paul Wheelhouse introduced General Licence restrictions for shooting estates where police evidence confirmed that raptor persecution had taken place but where there was insufficient evidence to bring a prosecution against a named individual. This was supposed to be a ‘reputational driver’ to deter crimes but has proven to be utterly ineffective with just a handful of restrictions applied over the last seven years and most ‘sanctioned’ estates simply given an individual licence to allow them to continue the activities which were supposed to have been restricted under the General Licence. It’s just bonkers.
Also in 2014, Paul Wheelhouse ordered a review of gamebird management systems in other European countries to see whether these different management approaches could help address ongoing raptor persecution in Scotland.
Also in 2014, the Scottish Government finally launched a public consultation on increased powers for the SSPCA, three years after first agreeing to set this up.
In 2014, Mark Avery and Chris Packham launched the concept of Hen Harrier Day to draw attention to the plight of the hen harrier, timed to coincide with the start of the grouse shooting season on 12th August. Hen Harrier Day has now become an annual event and volunteers Andrea Hudspeth and Andrea Goddard have organised these high profile events in Scotland.
In 2015, with raptor poisoning crimes still occurring, not content that the poisoners had already been given an opportunity to hand in their illegal stashes back in 2011, the Scottish Government launched its second poisons amnesty scheme, ten years after it became an offence to possess these dangerous toxins. How many chances do these gamekeepers get?
Also in 2015, SNH launched its ridiculous Heads up for Hen Harriers project – joining forces with shooting estates to fix nest cameras at hen harrier nests to determine the cause of breeding failures on grouse moors (yes, really!). It was doomed to failure because obviously the gamekeepers on estates where the cameras had been installed would not destroy the harriers/nests (at least not while the birds were within camera range) and the study’s ‘findings’ would then be skewed towards natural predator events and poor weather conditions which the grouse shooting industry would then point to as being the main cause of hen harrier breeding failure on grouse moors. It was nothing more than a greenwashing project.
Also in 2015, Scottish Environment LINK published a damning report demonstrating that wildlife crime enforcement measures were still weak, inconsistent & ineffective, seven years after the HM Inspector of Constabulary published its Thematic Review into the prevention, investigation and prosecution of wildlife crime and its subsequent recommendations to improve enforcement measures. Even today, apart from the RSPB’s meticulous records, it’s virtually impossible to get accurate raptor persecution statistics due to incoherent recording across agencies and Police Scotland’s strange decisions to sometimes withhold information, long after investigations have closed.
Also in 2015, Professor Poustie’s review of wildlife crime penalties was published, making a series of recommendations to substantially increase penalties for certain types of wildlife crime, including raptor persecution.
A year later in 2016, then Environment Minister Dr Aileen McLeod accepted the Poustie Review recommendations to substantially increase penalties for wildlife crime. These were not finally enacted until four years later in the Animals and Wildlife (Penalties, Protections and Powers) (Scotland) Act 2020, increasing the maximum penalty for the most serious animal welfare and wildlife crimes to five years imprisonment and unlimited fines. We have yet to see these utilised by the courts.
Also in 2016 the Scottish Government made a manifesto pledge to establish a Wildlife Crime Investigation Unit as part of Police Scotland. This has not happened and appears to have been quietly dropped.
Also in 2016, the Scottish Raptor Study Group (SRSG) launched a petition to the Scottish Parliament calling for the introduction of a state-regulated licensing system for gamebird shooting. These volunteers who later spoke so passionately and convincingly in front of a televised Parliamentary committee in 2017 were subjected to a barrage of offensive online abuse from a number of gamekeepers and their hangers-on and this hate campaign continues to this day.
[SRSG members Patrick Stirling-Aird, Andrea Hudspeth, Logan Steele and Duncan Orr-Ewing outside the Scottish Parliament building. Photo by SRSG]
2016 also saw what in my opinion was the most significant and important event in the road leading to the introduction of grouse moor licensing. The RSPB published a press release about the suspicious disappearance of eight satellite-tagged golden eagles on grouse moors in the Monadhliaths between 2011-2016. Public outrage about this news, combined with the fact that nobody had ever being successfully prosecuted for killing a golden eagle, led to then Environment Cabinet Secretary Roseanna Cunningham calling for a review of golden eagle satellite tag data to establish whether there was a pattern to the disappearance of tagged eagles and whether there was a link with driven grouse shooting. Of course we all knew there was, but it was significant that the Cabinet Secretary had officially requested the analysis. Predictably, this Government-sponsored review coincided with a concerted smear campaign by the grouse shooting industry to undermine the functionality and reliability of satellite tags and the integrity of the highly qualified and licensed researchers who were fitting the tags to eagles. This continues to this day.
In 2017 the review of gamebird management in other European countries was published, showing that gamebird shooting in the UK was the most unregulated and unaccountable system of all those reviewed. This didn’t result in any direct action from the Scottish Government other than an instruction for the Werritty panel to consider the report’s findings as part of its Grouse Moor Management Review.
Also in 2017 Cabinet Secretary Roseanna Cunningham responded to the public consultation on increased SSPCA powers (3 yrs after the consultation closed!) & rejected it ‘based on legal advice’ which was never explained. As an alternative, she announced a Police Special Constables pilot scheme in the Cairngorms National Park to help detect raptor persecution crimes and bring the offenders before the courts.
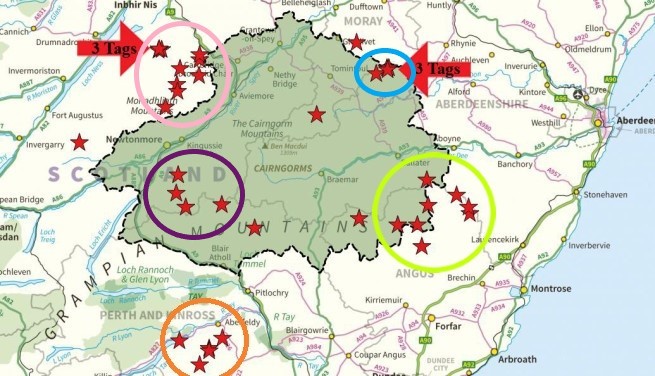
The most significant event in 2017 was the publication of the Golden Eagle Satellite Tag Review. This comprehensive and forensic review was devastating, showing that almost one third of satellite-tagged golden eagles (131 of them) had been illegally killed or had ‘disappeared’ in suspicious circumstances between 2004-2016, and there were irrefutable geographic clusters centred on some driven grouse moors:
On the basis of this report, Cabinet Secretary Roseanna Cunningham ordered yet another independent review, this time to assess the environmental impact of grouse moor management and to provide recommendations and options for regulation, including the potential for a licensing scheme. Professor Werritty was appointed to lead the review.
In 2018 REVIVE was launched – a consortium of environmental, social justice and animal welfare groups seeking grouse moor reform in Scotland. The well-attended launch took place in Edinburgh and Chris Packham was the keynote speaker. Inevitably this led to yet another smear campaign by certain elements of the grouse shooting industry which continues to this day.
[Photo by REVIVE]
In 2019 the Police Special Constables pilot scheme in the Cairngorms National Park came to an end in complete failure. They didn’t report a single wildlife crime during this two-year scheme but illegal raptor persecution continued, as evidenced by the RSPB’S annual reports.
In December 2019 the Werritty Report was finally published two and a half years after it was commissioned. It highlighted many of the problems associated with driven grouse moor management but crucially it recommended a further five-year wait before the introduction of a licensing scheme to allow the grouse shooting industry yet more opportunity to oust the criminals within rather than have regulation foisted on it by legislation. This recommendation was clearly a result of having a number of representatives from the grouse shooting industry serving on the so-called independent panel. Meanwhile, the raptor killing continued.
In 2020 MSP Mark Ruskell (Scottish Greens) proposed increased powers for the SSPCA as an amendment in the Animals & Wildlife Bill. The then Environment Minister Mairi Gougeon rejected the amendment but promised to establish a task force later in summer to consider increased powers. Deja vu, anyone?
In November 2020 the Animals and Wildlife (Penalties, Protections and Powers) (Scotland) Act was enacted, increasing the maximum penalty for the most serious animal welfare and wildlife crimes to five years imprisonment and unlimited fines (after the recommendations of the Poustie review published in 2015). This raises the status of some offences to ‘serious’ and thus for the first time allows the Police to seek permission to utilise covert video surveillance in areas where raptor persecution is suspected. I know there is enthusiasm for this from a number of police officers and I look forward to seeing some results.
In December 2020, a year after receiving the Werrity Review, Environment Minister Mairi Gougeon announced the Scottish Government’s intention to introduce a licensing scheme for grouse moors without waiting for a further five years as the review had recommended.
[NB: I understand that Ian Thomson, Head of Investigations at RSPB Scotland will publish a blog later today (26th November 2021) detailing what has happened in the year following this announcement. I will publish the blog here when it’s available]. Update – Ian’s blog available here
In January 2021 the new Environment Minister Ben MacPherson responded to a Parliamentary Question from Mark Ruskell MSP and admits that the promised taskforce to consider increased powers for the SSPCA had not yet formed but was ‘expected later this year’. This is ten years on from when increased powers for the SSPCA was first mooted in the Scottish Parliament.
In September 2021 the Scottish Government published its five-year Programme for Government and it included commitments to deliver the recommendations of the Werritty review, and to establish a taskforce to review increased powers for the SSPCA, to report by the end of 2022. Yet another Environment Minister (the 9th one?) is in post – Mairi McAllan.
In October 2021 the ridiculous Heads Up for Hen Harriers ‘partnership’ project was closed, with SNH declaring it a ‘success’. It wasn’t, at all. I’ll be blogging about this separately in the next few days.
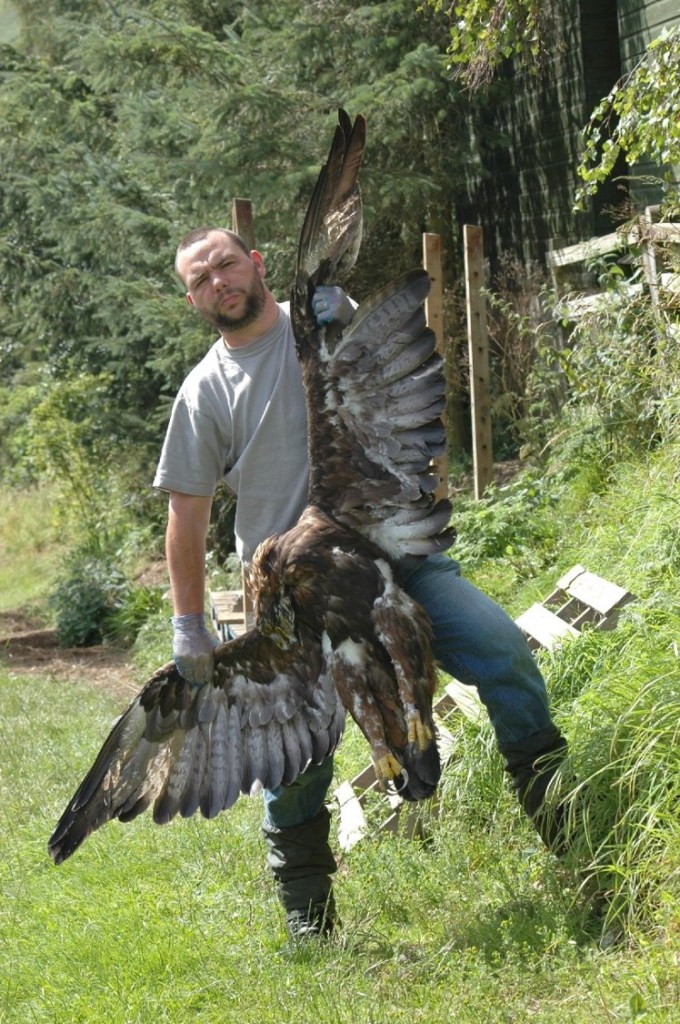
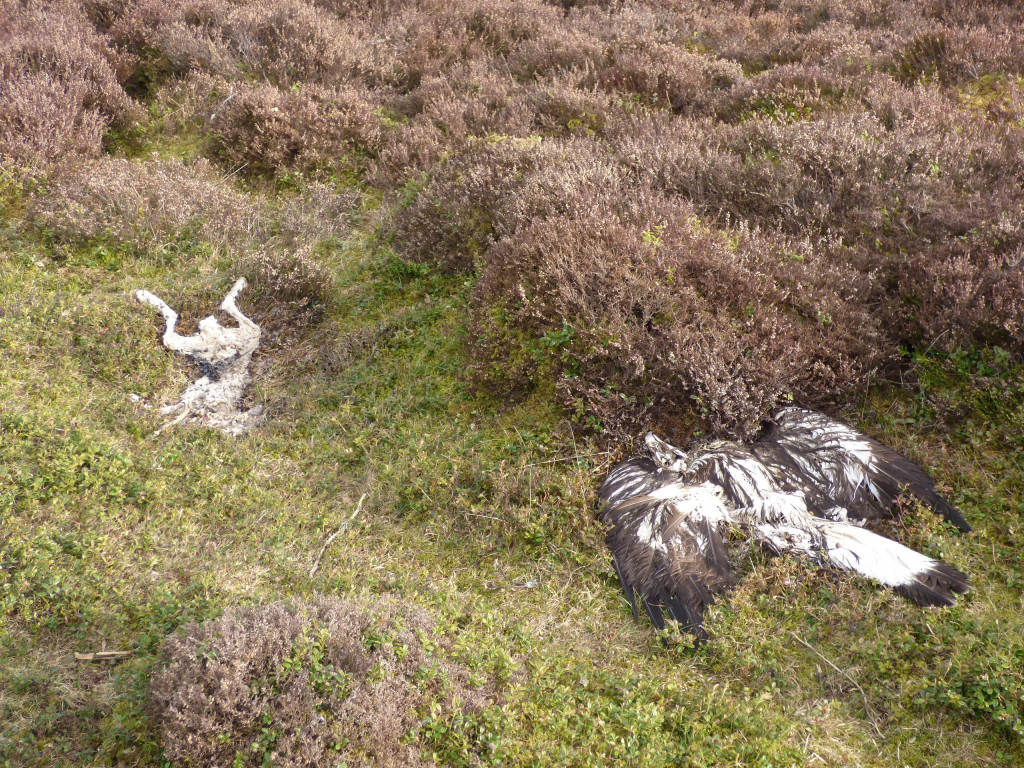
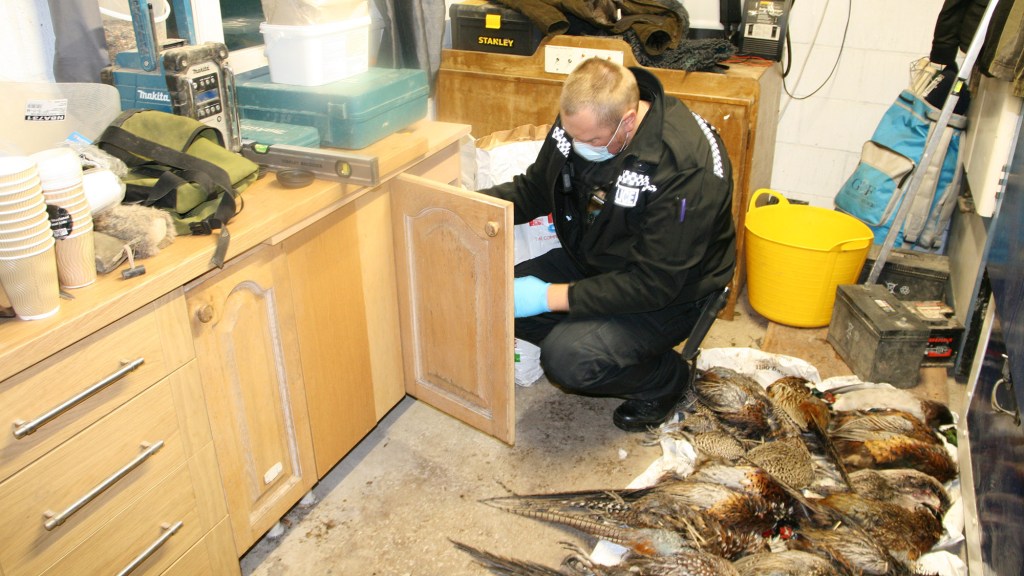
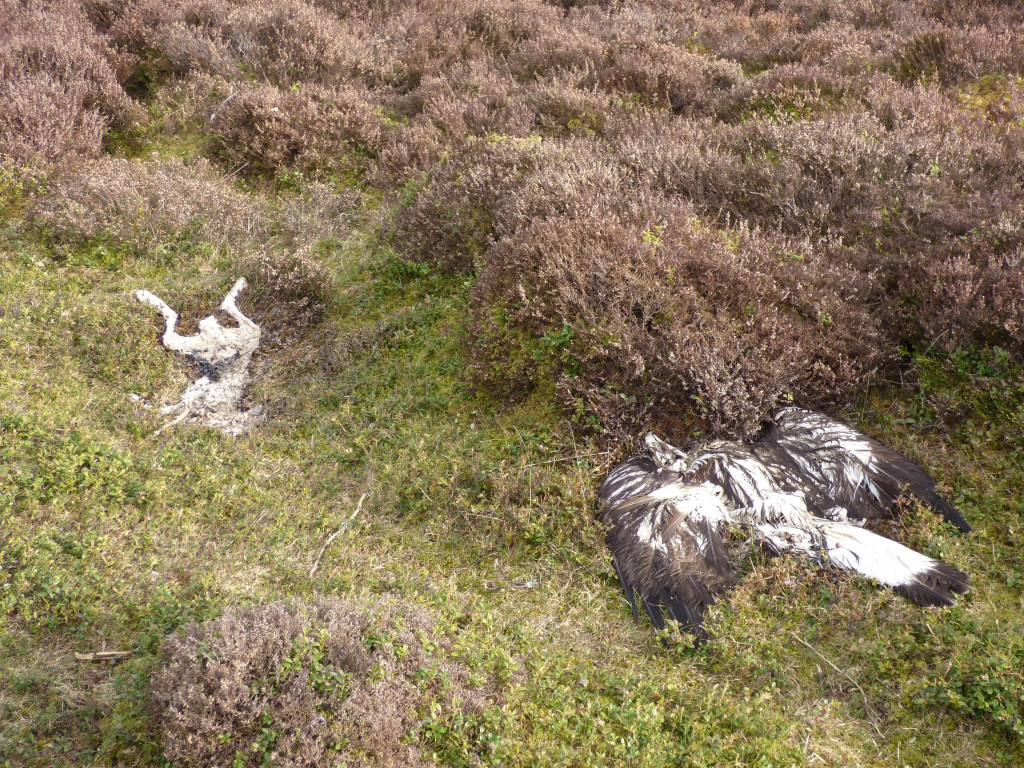
Meanwhile, in May 2021 a young golden eagle was found deliberately poisoned, lying dead next to a poisoned bait, on an Invercauld Estate grouse moor inside the Cairngorms National Park. Sixty-seven years after raptors gained legal protection and 23 years after Donald Dewar declared raptor persecution in Scotland ‘a national disgrace’, golden eagles and other raptors are still being illegally killed on some driven grouse moors.
[The poisoned golden eagle, next to the poisoned hare bait, on a grouse moor on Invercauld Estate in the Cairngorms National Park in May 2021. Photo by RSPB Scotland]
So despite all this campaigning and political movement, nothing has changed on the ground. Golden eagles (and other raptor species) are still being killed on grouse moors, even inside the Cairngorms National Park, and still not one person has been successfully prosecuted.
It’s shameful that we, ordinary members of the public, have to campaign just to have the law upheld, but its even more shameful that despite decades of compelling evidence, the Scottish Government has still not taken effective action against the criminals within the driven grouse shooting industry.
Even so, we should absolutely celebrate how far we have come, and it’s been hard work and at great personal cost to many, but don’t underestimate just how much more work there is to come.