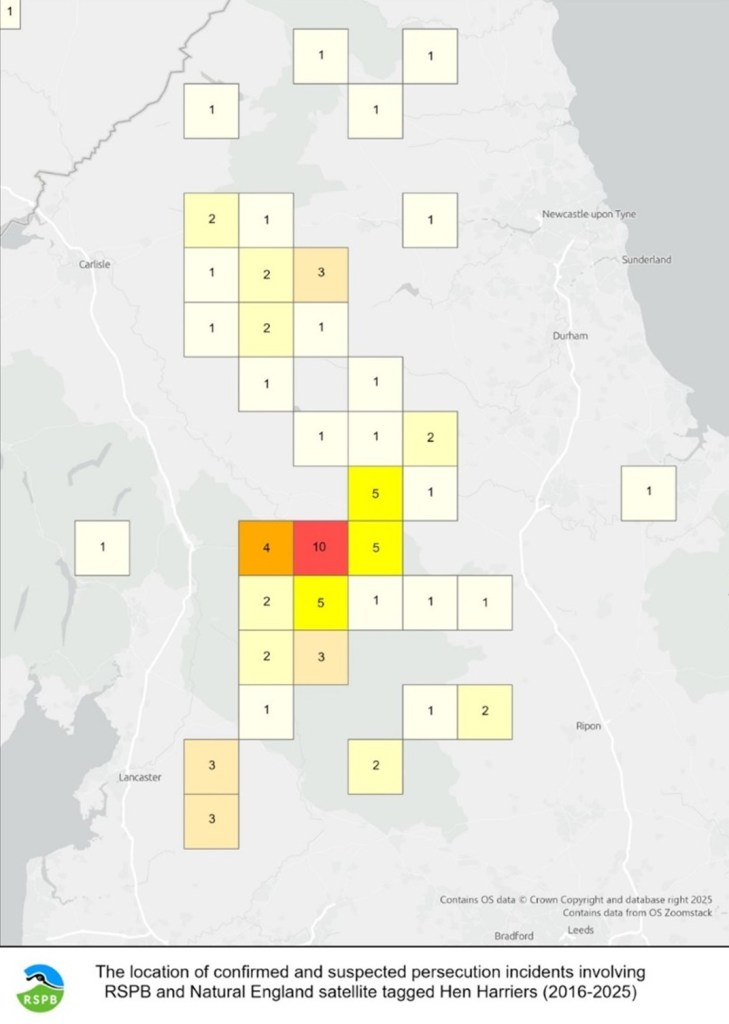
For anyone who still wants to pretend that the grouse shooting industry isn’t responsible for the systematic extermination of Hen Harriers on grouse moors across the UK, here’s the latest catalogue of crime that suggests otherwise.

This is the blog I now publish after every reported killing or suspicious disappearance.
“They disappear in the same way political dissidents in authoritarian dictatorships have disappeared” (Stephen Barlow, 22 January 2021).
Today the list has been revised to reflect updates in various reports since I last updated the list in July 2025. There isn’t a one-stop shop (apart from this list) where you can find information about ‘missing’ or illegally killed Hen Harriers – the information for this list is sourced and cross-referenced from various places, including Natural England’s database, the RSPB’s database, the HSE’s database, police reports, RSPB Birdcrime reports and FoIs to various agencies. This list doesn’t include any Hen Harriers that have been listed as having a natural cause of death (e.g. known/suspected predation), or listed as ‘likely tag failure’, or known to have been lost abroad, or where the cause of death is inconclusive, unless there is additional information (e.g. from satellite tag data) which indicates suspicious or illegal activity. It is painstaking work that takes a lot of time to complete, but I consider it to be as accurate and comprehensive as it can be at the time of writing.
I’ve been compiling this list only since 2018 because that is the year that the grouse shooting industry ‘leaders’ would have us believe that the criminal persecution of Hen Harriers had stopped and that these birds were being welcomed back on to the UK’s grouse moors (see here).
This assertion was made shortly before the publication of a devastating new scientific paper that demonstrated that 72% of satellite-tagged Hen Harriers were confirmed or considered likely to have been illegally killed, and this was ten times more likely to occur over areas of land managed for grouse shooting relative to other land uses (see here). A further scientific paper published in 2023 by scientists at the RSPB, utilising even more recent data, echoed these results – see here.
2018 was also the year that Natural England issued a licence to begin a Hen Harrier brood meddling trial on grouse moors in northern England. For new blog readers, Hen Harrier brood meddling was a conservation sham sanctioned by DEFRA as part of its ludicrous ‘Hen Harrier Action Plan‘ and carried out by Natural England (NE), in cahoots with the very industry responsible for the species’ catastrophic decline in England.
For more background see here and for a critical evaluation of the trial after 5 years see this report by Wild Justice. In 2024 the brood meddling trial appeared to collapse for reasons which are not yet clear (see here) and the licence for the so-called ‘scientific trial’ expired. In March 2025 Natural England announced the end of the brood meddling trial (here) and in April 2025 announced that a licence application to continue brood meddling, submitted by the Moorland Association, had been refused (here).
Brood meddling was earlier described as a sort of ‘gentleman’s agreement’ by commentator Stephen Welch:
“I don’t get it, I thought the idea of that scheme was some kind of trade off – a gentleman’s agreement that the birds would be left in peace if they were moved from grouse moors at a certain density. It seems that one party is not keeping their side of the bargain“.
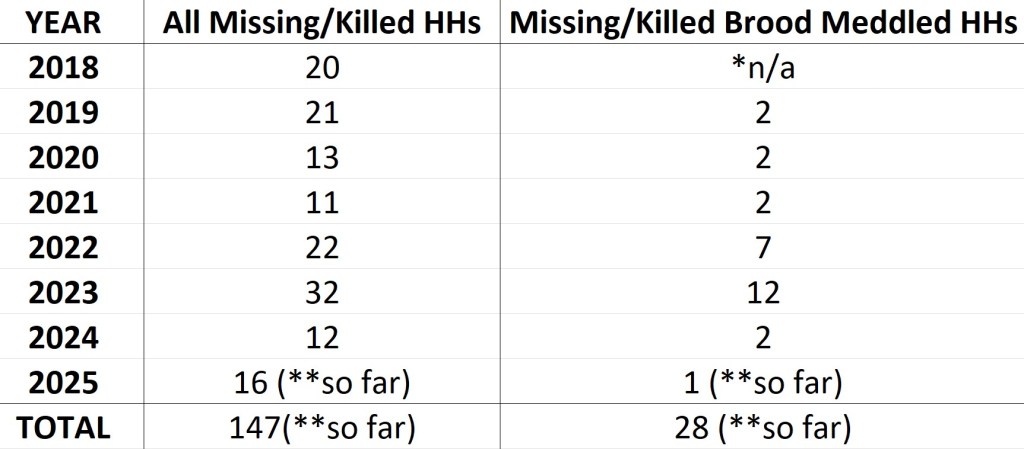
With at least 147 Hen Harriers gone since 2018, and 28 of those being brood meddled birds, there is no question that the grouse shooting industry was simply taking the piss. Meanwhile, Natural England pretended that ‘partnership working’ was the way to go and consecutive Tory DEFRA Ministers remained silent for all those years.
**There are a number of suspected Hen Harrier persecution incidents from 2025 not yet in the public domain & currently subject to ongoing police investigation. These are not included here.
‘Partnership working’ according to Natural England appeared to include authorising the removal of Hen Harrier chicks from a grouse moor already under investigation by the police for suspected raptor persecution (here) and accepting a £75k ‘donation’ from representatives of the grouse shooting industry with a contract clause that prevented Natural England from criticising them or the sham brood meddling trial (see here). This was in addition to a further £10k ‘donation’ that Natural England accepted, under the same terms, in 2021 (here).
Thankfully, the Scottish Government finally decided to act by introducing a grouse moor licensing scheme under the Wildlife Management & Muirburn (Scotland) Act 2024. The intention behind this new legislation is that grouse shooting estates could have their licences suspended/revoked if, on the balance of probability, it is shown that any raptor persecution crimes (& some other associated offences) are linked with grouse moor management on that estate. There were, however, ongoing issues with the licence as it was significantly watered-down after an intervention from the grouse shooting industry (see here). Efforts to close this loophole are included in the Natural Environment (Scotland) Bill, currently making its way through the Scottish Parliament (here).
In England a new Hen Harrier Taskforce was established in 2024, led by the National Wildlife Crime Unit, to use innovative techniques to target Hen Harrier persecution hotspots (locations where Hen Harriers repeatedly ‘disappear’ or are found illegally killed). It’s too early to judge the Taskforce’s success/failure and it’s been met with considerable resistance from the Moorland Association, the grouse moor owners’ lobby group (e.g. see here). So far though, it’s quite clear that the the illegal killing continues.
So here’s the latest gruesome list of ‘missing’/illegally killed Hen Harriers since 2018. Note that the majority of these birds (but not all) were fitted with satellite tags. How many more [untagged] harriers have been killed? We now have evidence that gamekeepers are specifically targeting untagged Hen Harriers, precisely to avoid detection (see here for extraordinary footage/audio captured by the RSPB’s Investigations Team as featured on Channel 4 News in October 2024).
2018
February 2018: Hen Harrier Saorsa ‘disappeared’ in the Angus Glens in Scotland (here). The Scottish Gamekeepers Association later published wholly inaccurate information claiming the bird had been re-sighted. The RSPB dismissed this as “completely false” (here). Tagged by RSPB.
5 February 2018: Hen Harrier Marc ‘disappeared’ on a grouse moor in Durham (here). Tagged by RSPB.
9 February 2018: Hen Harrier Aalin ‘disappeared’ on a grouse moor in Wales (here). Tagged by RSPB.
March 2018: Hen Harrier Blue ‘disappeared’ in the Lake District National Park (here). Tagged by RSPB.
March 2018: Hen Harrier Finn ‘disappeared’ near Moffat in Scotland (here). Tagged by RSPB.
18 April 2018: Hen Harrier Lia ‘disappeared’ in Wales and her corpse was retrieved in a field in May 2018. Cause of death was unconfirmed but police treating death as suspicious (here). Tagged by RSPB.
8 August 2018: Hen Harrier Hilma ‘disappeared’ on a grouse moor in Northumberland (here). Tagged by RSPB.
16 August 2018: Hen Harrier Athena ‘disappeared’ on a grouse moor in Scotland (here). Tagged by RSPB.
26 August 2018: Hen Harrier Octavia ‘disappeared’ on a grouse moor in the Peak District National Park (here). Tagged by RSPB.
29 August 2018: Hen Harrier Margot ‘disappeared’ on a grouse moor in Scotland (here). Tagged by RSPB.
29 August 2018: Hen Harrier Heulwen ‘disappeared’ on a grouse moor in Wales (here). Tagged by RSPB.
3 September 2018: Hen Harrier Stelmaria ‘disappeared’ on a grouse moor in Scotland (here). Tagged by RSPB.
24 September 2018: Hen Harrier Heather ‘disappeared’ on a grouse moor in Scotland (here). Tagged by RSPB.
2 October 2018: Hen Harrier Mabel (Tag ID 34342) ‘disappeared’ on a grouse moor on the edge of the Yorkshire Dales National Park (here). Grid ref NY851059. Tagged by NE.
3 October 2018: Hen Harrier Thor ‘disappeared’ next to a grouse moor in Bowland, Lanacashire (here). Tagged by RSPB.
23 October 2018: Hen Harrier Tom (Tag ID 161144) ‘disappeared’ in South Wales (here). Grid ref SS906698. Tagged by NE.
26 October 2018: Hen Harrier Arthur ‘disappeared’ on a grouse moor in the North York Moors National Park (here). Tagged by RSPB.
1 November 2018: Hen Harrier Barney (Tag ID 34343) ‘disappeared’ on Bodmin Moor, Cornwall (here). Grid ref SX140720. Tagged by NE.
10 November 2018: Hen Harrier Rannoch ‘disappeared’ on a grouse moor in Scotland (here). Her corpse was found nearby in May 2019 – she’d been killed in an illegally-set spring trap (here). Tagged by RSPB.
14 November 2018: Hen Harrier River ‘disappeared’ on a grouse moor in the Nidderdale AONB (here). Her corpse was found nearby in April 2019 – she’d been illegally shot (here). Tagged by RSPB.
2019
16 January 2019: Hen Harrier Vulcan ‘disappeared’ in Wiltshire close to Natural England’s proposed reintroduction site (here). Tagged by RSPB.
28 January 2019: Hen Harrier DeeCee ‘disappeared’ in Glen Esk, a grouse moor area of the Angus Glens (see here). Tagged by RSPB.
7 February 2019: Hen Harrier Skylar ‘disappeared’ next to a grouse moor in South Lanarkshire (here). Tagged by RSPB.
22 April 2019: Hen Harrier Marci ‘disappeared’ on a grouse moor in the Cairngorms National Park (here). Tagged by RSPB.
26 April 2019: Hen Harrier Rain ‘disappeared’ on a grouse moor in Nairnshire (here). Tagged by RSPB.
11 May 2019: An untagged male Hen Harrier was caught in an illegally-set trap next to his nest on a grouse moor in South Lanarkshire. He didn’t survive (here).
7 June 2019: An untagged Hen Harrier was found dead on a grouse moor in Scotland. A post mortem stated the bird had died as a result of ‘penetrating trauma’ injuries and that this bird had previously been shot (here).
5 September 2019: Wildland Hen Harrier 1 ‘disappeared’ on a grouse moor nr Dalnaspidal on the edge of the Cairngorms National Park (here). Tagged by Wildlands.
11 September 2019: Hen Harrier Romario ‘disappeared’ on a grouse moor in the Cairngorms National Park (here). Tagged by RSPB.
14 September 2019: Hen Harrier R1-M2-19 (Brood meddled in 2019, Tag ID 183704) ‘disappeared’ in the North Pennines (here). Grid ref SD920943. Tagged by NE.
23 September 2019: Hen Harrier R1-M4-19 (Brood meddled in 2019, Tag ID 55149) ‘disappeared’ in North Pennines (here). Grid ref NY952103. Tagged by NE.
24 September 2019: Wildland Hen Harrier 2 ‘disappeared’ on a grouse moor at Invercauld in the Cairngorms National Park (here). Tagged by Wildlands.
24 September 2019: Hen Harrier Bronwyn ‘disappeared’ near a grouse moor in North Wales (here). Tagged by RSPB.
10 October 2019: Hen Harrier Ada ‘disappeared’ on a grouse moor in the North Pennines AONB (here). Tagged by RSPB.
12 October 2019: Hen Harrier Thistle ‘disappeared’ on a grouse moor in Sutherland (here). Tagged by RSPB.
18 October 2019: Member of the public reports the witnessed shooting of an untagged male Hen Harrier on White Syke Hill in North Yorkshire (here).
November 2019: Hen Harrier Mary found illegally poisoned on a pheasant shoot in Ireland (here). Tagged by RSPB.
November 2019: Hen Harrier Artemis ‘disappeared’ near Long Formacus in south Scotland (here). Tagged by RSPB.
14 December 2019: Hen harrier Oscar ‘disappeared’ in Eskdalemuir, south Scotland (here). Tagged by RSPB.
December 2019: Hen Harrier Ingmar ‘disappeared’ in the Strathbraan grouse moor area of Perthshire (here). Tagged by RSPB.
Unknown date in 2019: Hen Harrier Erin tagged on Isle of Man ‘disappeared’ (Stop No Malfunction) – location unknown (see here). Tagged by RSPB.
2020
27 January 2020: Members of the public report the witnessed shooting of a male Hen Harrier on Threshfield Moor in the Yorkshire Dales National Park (here).
5 April 2020: Hen Harrier Hoolie ‘disappeared’ on a grouse moor in the Cairngorms National Park (here). Tagged by RSPB.
8 April 2020: Hen Harrier Marlin ‘disappeared’ on a grouse moor in the Cairngorms National Park (here). Tagged by RSPB.
19 May 2020: Hen Harrier Fingal ‘disappeared’ on a grouse moor in the Lowther Hills, Scotland (here). Tagged by RSPB.
21 May 2020: Hen Harrier R1-M1-19 (Brood meddled in 2019, Tag ID 183701) ‘disappeared’ on a grouse moor in Cumbria shortly after returning from wintering in France (here). Grid ref SD770877. Tagged by NE.
27 May 2020: Hen Harrier Silver ‘disappeared’ on a grouse moor on Leadhills Estate, Scotland (here). Tagged by RSPB.
2020: day/month unknown: Unnamed male Hen Harrier breeding on RSPB Geltsdale Reserve, Cumbria ‘disappeared’ while away hunting (here).
14 August 2020: Hen Harrier Solo (Tag ID 201119) ‘disappeared’ in confidential nest area in Lancashire (here). Tagged by NE.
7 September 2020: Hen Harrier Dryad ‘disappeared’ on a grouse moor in the Yorkshire Dales National Park (here). Tagged by RSPB.
16 September 2020: Hen Harrier Fortune (Tag ID 162150a) ‘disappeared’ from a confidential roost site in Northumberland (here). Tagged by NE.
19 September 2020: Hen Harrier Harold (Tag ID 57272) ‘disappeared’ on a grouse moor in the Yorkshire Dales National Park (here). Grid ref NY830036. Tagged by NE.
20 September 2020: Hen Harrier R1-M4-20 (Brood meddled in 2020, Tag ID 55152) ‘disappeared’ next to a grouse moor in North Yorkshire (here). Grid ref SE103956. Tagged by NE.
19 December 2020: Hen Harrier Lagertha (Tag ID 201126a) ‘disappeared’ in Christchurch, Dorset close to winter roost. Not to be confused with RSPB-tagged bird also called Lagertha (2023). Grid ref SZ161924. Tagged by NE.
2021
24 February 2021: Hen Harrier Tarras ‘disappeared’ next to a grouse moor in Northumberland (here). Tagged by RSPB.
12th April 2021: Hen Harrier Yarrow ‘disappeared’ near Stockton, County Durham (here). Tagged by RSPB.
18 May 2021: Untagged breeding male Hen Harrier (Geltsdale 1) ‘disappeared’ from its breeding attempt on RSPB Geltsdale Reserve, Cumbria whilst away hunting (here).
18 May 2021: Another untagged breeding male Hen Harrier (Geltsdale 2) ‘disappeared’ from its breeding attempt on RSPB Geltsdale Reserve, Cumbria whilst away hunting (here).
24 July 2021: Hen Harrier Asta (Tag ID 201117) ‘disappeared’ in the North Pennines after establishing a home range around Gilmonby Moor (here). We learned 18 months later that her wings had been ripped off so her tag could be fitted to a crow in an attempt to cover up her death (here). Grid ref SE206937. Tagged by NE.
14th August 2021: Hen Harrier Josephine (Tag ID 213850) ‘disappeared’ at a ‘confidential site’ in Northumberland (here). Grid ref NY592841. Tagged by NE.
17 September 2021: Hen Harrier Reiver ‘disappeared’ in a grouse moor dominated region of Northumberland (here). Tagged by RSPB.
24 September 2021: Hen Harrier R2-F1-21 (Brood meddled in 2021, Tag ID 213918) ‘disappeared’ in Northumberland (here). Grid ref NZ022667. Tagged by NE.
15 November 2021: Hen Harrier R2-F1-20 (Brood meddled in 2020, Tag ID 203003) ‘disappeared’ at the edge of a grouse moor on Arkengarthdale Estate in the Yorkshire Dales National Park (here). Grid ref NY959039. Tagged by NE.
12 December 2021: Hen Harrier Jasmine (Tag ID 213848) ‘disappeared’ on a grouse moor (High Rigg Moor on the Middlesmoor Estate) in the Nidderdale AONB in North Yorkshire (here). Grid ref SE034733. Tagged by NE.
Unknown date in 2021: Hen Harrier Maiden, tagged in Lancashire in 2021, ‘disappeared’ at unknown location (here). Tagged by RSPB.
2022
9 January 2022: Hen Harrier Ethel (Tag ID 213852) ‘disappeared’ in Northumberland (here). Grid ref NY936632. Tagged by NE.
10 February 2022: An unnamed satellite-tagged Hen Harrier ‘disappeared’ in a grouse moor dominated area of the Peak District National Park (here). One year later it was revealed that the satellite tag/harness of this young male called ‘Anu’ had been deliberately cut off (see here). Tagged by RSPB.
12 April 2022: Hen Harrier Free (Tag ID 201121) ‘disappeared’ at a ‘confidential site’ in Cumbria (here). It later emerged he hadn’t disappeared, but his mutilated corpse was found on moorland in the Yorkshire Dales National Park. A post mortem revealed the cause of death was having his head twisted and pulled off. One (ringed) leg had also been torn off whilst he was still alive (here). Tagged by NE.
April 2022: Hen Harrier Pegasus ‘disappeared’ on a grouse moor at Birkdale in the Yorkshire Dales National Park (here). Tagged by RSPB.
May 2022: An untagged breeding male Hen Harrier (Peak District 1) ‘disappeared’ from a National Trust-owned grouse moor in the Peak District National Park (here).
May 2022: Another untagged breeding male Hen Harrier (Peak District 2) ‘disappeared’ from a National Trust-owned grouse moor in the Peak District National Park (here).
14 May 2022: Hen Harrier Harvey (Tag ID 213844) ‘disappeared’ in the North Pennines (here). Grid ref NY918019. Tagged by NE.
20 June 2022: Hen harrier chick #1 stamped to death in nest on a grouse moor in the Yorkshire Dales National Park (here).
20 June 2022: Hen Harrier chick #2 stamped to death in nest on a grouse moor in the Yorkshire Dales National Park (here).
20 June 2022: Hen Harrier chick #3 stamped to death in nest on a grouse moor in the Yorkshire Dales National Park (here).
20 June 2022: Hen Harrier chick #4 stamped to death in nest on a grouse moor in the Yorkshire Dales National Park (here).
17 August 2022: Hen Harrier R1-M1-22 (Brood meddled in 2022, Tag ID 232637) ‘disappeared’ on moorland in the Yorkshire Dales National Park (here). Grid ref SD804893. Tagged by NE.
September 2022: Hen Harrier Sullis ‘disappeared’ on a grouse moor in Cumbria (here). Tagged by RSPB.
5 October 2022: Hen Harrier R3-M2-22 (Brood meddled in 2022, Tag ID 213920a) ‘disappeared’ on moorland in the Yorkshire Dales National Park (here). Grid ref NY791016. Tagged by NE.
10 October 2022: Hen Harrier Sia ‘disappeared’ near Hamsterley Forest in the North Pennines (here). Tagged by RSPB.
October 2022: Hen Harrier R1-F1-21 (Brood meddled in 2021, Tag ID 213919) ‘disappeared’ in the North Sea off the North York Moors National Park (here). Tagged by NE.
1 December 2022: Hen Harrier R1-M1-21 (Brood meddled in 2021, Tag ID 55145a) ‘disappeared’ on moorland in the Yorkshire Dales National Park (here). Grid ref SD917620. Tagged by NE.
7 December 2022: Hen Harrier R2-F2-20 (Brood meddled in 2020, Tag ID 55144) ‘disappeared’ from winter roost (same as R3-F1-22) on moorland in North Pennines AONB. Later found dead on 26 June 2023 with 3 shotgun pellets in corpse (here). Grid ref NY730372. Tagged by NE.
14 December 2022: Hen Harrier R3-F1-22 (Brood meddled in 2022, Tag ID 213921a) ‘disappeared’ from winter roost (same as R2-F2-20) on moorland in the North Pennines AONB (here). Later found dead on 10 April 2023 with two shotgun pellets in corpse (here). Grid ref NY708423. Tagged by NE.
15 December 2022: Hen Harrier R2-F1-22 (Brood meddled in 2022, Tag ID 213931) ‘disappeared’ on moorland in the Yorkshire Dales National Park (here). Grid ref SD847831. Tagged by NE.
Unknown date in 2022: Hen Harrier Heath, tagged in Lancashire in 2019, ‘disappeared’ at unknown location (here). Tagged by RSPB.
Unknown date in 2022: Hen Harrier Syrcas, tagged in Conwy in 2021, ‘disappeared’ at unknown location (here). Tagged by RSPB.
2023
30 March 2023: Hen Harrier R1-F3-22 (Brood meddled in 2022, Tag ID NY823039) ‘disappeared’ in Yorkshire (here). Grid ref NY823039. Tagged by NE.
March 2023: Hen Harrier (tagged), last transmission/sighting in Lancashire. No tag number provided. Reported in RSPB Birdcrime 2023, Appendix 4 (here).
1 April 2023: Hen Harrier R2-M1-22 (Brood meddled in 2022, Tag ID NY846027) ‘disappeared’ in Yorkshire (here). Grid ref NY846027. Tagged by NE.
April 2023: Hen Harrier Lagertha ‘disappeared’ in North Yorkshire (here). Tagged by RSPB. Not to be confused with Lagertha tagged by NE & disappeared in 2020).
April 2023: Hen Harrier Nicola (Tag ID 234078) ‘disappeared’ in North Yorkshire (here). Grid ref SD831860. Tagged by NE.
April 2023: Untagged male Hen Harrier (Geltsdale 3) ‘disappeared’ from an active nest on RSPB Geltsdale Reserve in Cumbria (here).
April 2023: Another untagged male Hen Harrier (Geltsdale 4) ‘disappeared’ from an active nest on RSPB Geltsdale Reserve in Cumbria (here).
April 2023: Untagged male Hen Harrier ‘disappeared’ from an active nest in Co Durham (here).
4/5 May 2023: Hen Harrier Rush ‘disappeared’ from a grouse moor in Bowland AONB in Lancashire (here). Tagged by RSPB.
9/10 May 2023: Hen Harrier Dagda tagged in Lancashire in June 2022 and who was breeding on the RSPB’s Geltsdale Reserve in 2023 until he ‘disappeared’, only to be found dead on the neighbouring Knarsdale grouse moor in May 2023 – a post mortem revealed he had been shot (here). Tagged by RSPB.
17 May 2023: Hen Harrier Wayland ‘disappeared’ in the Clapham area of North Yorkshire, just north of the Bowland AONB (here). Tagged by RSPB.
31 May 2023: Hen Harrier R2-M3-22 (Brood meddled in 2022, Tag ID 213932) ‘disappeared’ in Northumberland (here). Grid ref NY765687. Tagged by NE.
11 June 2023: Hen Harrier R2-M1-21 (Brood meddled in 2021, Tag ID 213922) ‘disappeared’ in the Yorkshire Dales National Park (here). Grid ref NY757000. Tagged by NE.
12 June 2023: Hen Harrier R1-M2-20 (Brood meddled in 2020, Tag ID 203004) ‘disappeared’ on a grouse moor in Co. Durham (here). Grid ref NY976322. Tagged by NE.
6 July 2023: Hen Harrier Rubi (Tag ID 201124a) ‘disappeared’ on a grouse moor in Co. Durham (here). Grid ref NY911151. Tagged by NE.
23 July 2023: Hen Harrier R1-F1-23 (Brood meddled in 2023, Tag ID 55154a) ‘disappeared’ on a grouse moor in Co. Durham (close to where Rubi disappeared) (here). Grid ref NY910126. Tagged by NE.
9 August 2023: Hen Harrier Martha ‘disappeared’ on a grouse moor (Westburnhope Moor) near Hexham in the North Pennines (here). Tagged by RSPB.
11 August 2023: Hen Harrier Selena ‘disappeared’ on a grouse moor (Mossdale Moor) in the Yorkshire Dales National Park (here). Tagged by RSPB.
11 August 2023: Hen Harrier R3-F1-23 (Brood meddled in 2023, Tag ID 201118a) ‘disappeared’ in Co. Durham (here). Grid ref NZ072136. Tagged by NE.
15 August 2023: Hen Harrier Hepit ‘disappeared’ on a grouse moor (Birkdale Common) near Kirkby Stephen in the Yorkshire Dales National Park (here). Tagged by RSPB.
24 August 2023: Hen Harrier R1-F2-23 (Brood meddled in 2023, Tag ID 55155a) ‘disappeared’ in Northumberland (here). Grid ref NY679863. Tagged by NE.
August-Sept 2023: Hen Harrier Harmonia ‘disappeared’ in the Yorkshire Dales National Park (here). ‘Stop No Malfunction’. Tagged by RSPB.
September 2023: Hen Harrier Saranyu, tagged in Cumbria in June 2023, ‘disappeared’ in Durham in September 2023 (here). Tagged by RSPB.
September 2023: Hen Harrier Inger, tagged in Perthshire in July 2022, ‘disappeared’ on a grouse moor in the Angus Glens in September 2023 (here). Tagged by RSPB.
15 September 2023: Hen Harrier Rhys (Tag ID 213847a), tagged in Cumbria on 1st August 2023, ‘disappeared’ on a grouse moor in the Yorkshire Dales National Park (here). Grid ref SD798896. Tagged by NE.
24 September 2023: Hen Harrier R2-F2-23 (Brood meddled in 2023, Tag ID 213929) ‘disappeared’ in the North Pennines (here). Grid ref NY888062. Tagged by NE.
26 September 2023: Hen Harrier Hope, tagged in Cumbria on 21 July 2023, ‘disappeared’ next to a grouse moor in the Yorkshire Dales National Park (here). Grid ref SD801926. Tagged by NE.
4 October 2023: Hen Harrier R1-M3-20 (Brood meddled in 2020, Tag ID 55153) ‘disappeared’ in Co Durham (here). Grid ref NY935192. Tagged by NE.
4 October 2023: Hen Harrier R4-F1-23 (Brood meddled in 2023, Tag ID 213925a) ‘disappeared’ on a grouse moor in the Yorkshire Dales National Park (here). Grid ref SE003981. Tagged by NE.
15 November 2023: Hen Harrier Hazel’ (Tag ID 240292) tagged in Cumbria on 21 July 2023, ‘disappeared’ on the Isle of Man (here). Grid ref SC251803. Tagged by NE.
7 December 2023: Hen Harrier R2-M1-20 (Brood meddled in 2020, Tag ID 55146a) ‘disappeared’ in Co Durham. Grid ref NY963211. Tagged by NE.
Unknown date in 2023: Hen Harrier Aurora, tagged in Dumfries & Galloway in 2022, ‘disappeared’ at unknown location (here). Tagged by RSPB.
2024
12 February 2024: Hen Harrier Susie (Tag ID 201122), found dead in Northumberland. Later revealed to have been the victim of shooting (here). Grid ref NY759585. Tagged by NE. Susie’s chicks were stamped to death at nest on moor at Whernside in 2022 (here).
15 February 2024: Hen Harrier Shalimar, tagged on the National Trust for Scotland’s Mar Lodge Estate in 2023, ‘disappeared’ in suspicious circumstances on a grouse moor in the notorious Angus Glens (here). Tagged by RSPB.
24 April 2024: Hen Harrier Ken (Tag ID 213849a) ‘disappeared’ in suspicious circumstances close to a grouse moor in Bowland (here). Grid ref SD684601. Tagged by NE.
17 May 2024: Hen Harrier R2-M2-23 (Brood meddled in 2023, Tag ID 213928) ‘disappeared’ in suspicious circumstances next to Middlesmoor grouse moor in Nidderdale (here). Grid ref SE043754. Tagged by NE.
7 June 2024: Hen Harrier Edna (Tag ID 161143a). Decomposed corpse found next to a wind farm nr Otterburn, Northumberland. Listed as ‘suspected illegally killed’. There has been a suggestion she was killed elsewhere & dumped at the wind farm as a ploy to cover up the crime (here). Grid ref NY910827. Tagged by NE.
25 June 2024: Hen Harrier R2-F1-23 (Brood meddled in 2023, Tag ID 213923) ‘disappeared’ in suspicious circumstances on a grouse moor in Yorkshire Dales National Park (here). Grid ref NY985082. Tagged by NE.
July 2024: Hen Harrier Helius, tagged in Lancashire in 2023, ‘disappeared’ in suspicious circumstances in Bowland (here). Tagged by RSPB.
29 July 2024: Hen Harrier (Tag ID 254843) tagged in Northumberland on 5 July 2024, decomposed corpse not suitable for post mortem but forensics work on her satellite tag showed shot damage (here). Grid ref NY824937. Tagged by NE.
October 2024: An un-tagged Hen Harrier was apparently shot on a grouse moor at Grassington in the Yorkshire Dales National Park by one of three gamekeepers being secretly filmed by the RSPB (here).
1 October 2024: Hen Harrier Dreich (Tag ID 254842) ‘disappeared’ in Lanarkshire (here). Grid ref NS826020. Tagged by NE.
15 October 2024: Hen Harrier Baldur (Tag ID 240291) ‘disappeared’ in Northumberland (here). Grid ref NZ038961. Tagged by NE.
19 October 2024: Hen Harrier Margaret (Tag ID 254844) ‘disappeared’ in Northumberland (here). It was later reported that her tag had been found (‘removed’) but no sign of the carcass (here). Grid ref NY878497. Tagged by NE.
2025
15 January 2025: Hen Harrier Red, hatched on the Tarras Valley Nature Reserve in 2024, ‘disappeared’ on a grouse moor in County Durham in the North Pennines, in the same area another tagged Hen Harrier (Sia) vanished in 2022 (here). Tagged by RSPB.
January 2025: Hen Harrier Ataksak was found poisoned close to a grouse moor in North Yorkshire (here). Apparently a police investigation is ongoing. Tagged by RSPB.
3 February 2025: Hen Harrier R3-F2-22 (Brood meddled in 2022, Tag ID 213924) ‘disappeared’ on a grouse moor in the North York Moors National Park (here). Grid ref SE759996. Tagged by NE.
27 February 2025: Hen Harrier Sita, tagged on behalf of Hen Harrier Action in Bowland in 2024 ‘disappeared’ from a roost site on a grouse moor in the Yorkshire Dales National Park (here). Tagged by RSPB.
4 April 2025: Hen Harrier Bonnie (Tag ID 254841) ‘disappeared’ on a grouse moor in the Moorfoots, Scotland (here). Grid ref NT415575. Tagged by NE.
10 April 2025: Hen Harrier Gill (Tag ID 240294) ‘disappeared’ in south Scotland (here). Grid ref NT440344. Tagged by NE.
1 May 2025: Hen Harrier Pete (Tag ID 213843) ‘disappeared’ in Cumbria (see here). Grid ref NY309418. Tagged by NE.
May 2025: Untagged Hen Harrier male (Geltsdale 5) with an active nest on RSPB Geltsdale Reserve in Cumbria ‘disappeared’. Strongly suspected to have been shot whilst away hunting on nearby grouse moor (here).
May 2025: Another untagged Hen Harrier male (Geltsdale 6) with another active nest on RSPB Geltsdale Reserve in Cumbria ‘disappeared’. Strongly suspected to have been shot whilst away hunting on nearby grouse moor (here).
May 2025: Hen Harrier Dynamo with an active nest on United Utilities-owned land in Bowland, Lancashire, ‘disappeared’. Strongly suspected to have been shot whilst away hunting on a nearby grouse moor (here). Tagged by RSPB.
May 2025: Untagged Hen Harrier with an active nest on United Utilities-owned land in Bowland, Lancashire, ‘disappeared’. Strongly suspected to have been shot whilst away hunting on a nearby grouse moor (here).
9 September 2025: Hen Harrier Maria (Tag ID 281718) tagged in Northumberland on 25 July 2025, ‘disappeared’ near Belford in Northumberland. Grid ref NU125340. Tagged by NE.
17 September 2025: Hen Harrier Beatrix, who fledged from the Tarras Valley Nature Reserve in summer 2025, ‘disappeared’ from an area dominated by grouse moors near Allendale in the North Pennines (here). Tagged by RSPB.
27 September 2025: Hen Harrier Wadrew, who fledged from the RSPB Geltsdale Reserve in Cumbria in summer 2025, ‘disappeared’ on a grouse moor near Birkdale in the Yorkshire Dales National Park (see here). Tagged by the RSPB.
30 September 2025: Hen Harrier Morrigan ‘disappeared’ in the southern area of the North Pennines National Landscape (here). Tagged by RSPB.
14 October 2025: Hen Harrier Circe, hatched on the Tarras Valley Nature Reserve in 2025 and tagged on behalf of charity Hen Harrier Action, ‘disappeared’ in the Moorfoots, south Scotland (here). Tagged by RSPB.
I’m aware of other tagged birds that went missing in 2025 and are not yet listed here as the incidents haven’t been made public as they’re the subject of active police investigations.
To be continued…
Of these 147 incidents, only one has resulted in an arrest and a subsequent prosecution (ongoing – after a ‘not guilty plea’ a gamekeeper is due in court again in January 2026, see here).
I had thought that when we reached 30 dead/missing Hen Harriers then the authorities might pretend to be interested and at least say a few words about this national scandal. We’ve now reached at least ONE HUNDRED AND FORTY SEVEN Hen Harriers, and still Govt ministers remain silent on the illegal persecution issue. They appear not to give a monkey’s. And yes, there are other things going on in the world, as always. That is not reason enough to ignore this blatant, brazen and systematic destruction of a supposedly protected species, being undertaken to satisfy the greed and bloodlust of a minority of society.
And let’s not forget the response from the (now former) Moorland Association Chair (and owner of Swinton Estate in North Yorkshire) Mark Cunliffe-Lister, who told BBC Radio 4 in August 2023 that, “Clearly any illegal [Hen Harrier] persecution is not happening” (here), in the year when a record 32 Hen Harriers had been confirmed ‘missing’ and/or illegally killed.
Nor should we forget the response from the Game and Wildlife Conservation Trust’s (GWCT) Director of Policy Dr Alistair Leake who wrote a letter to the Guardian newspaper in November 2023 stating that the Hen Harrier brood management [meddling] scheme “is surely a shining example of human / wildlife conflict resolution that would be the envy of other countries trying to find similar solutions“ (I kid you not – here).
Detective Inspector Mark Harrison of the National Wildlife Crime Unit (NWCU) who leads on the national Hen Harrier Taskforce will be giving a live online presentation on 27 January 2026 about the work being undertaken to tackle the ongoing illegal killing of Hen Harriers in the UK. More details here.
For new blog readers, an RSPB report Hen Harriers in the Firing Line, published last year provides a good overview of the illegal persecution of Hen Harriers on UK grouse moors, as does this news reel from Channel 4 News: