The BBC’s Highland Cops programme has entered its third series and episode 2 features the police investigation in to an active Goshawk nest that had been shot out on a sporting estate near Kingussie, on the western side of the Cairngorms National Park.
This investigation took place in June 2024 – see here for the police’s appeal for information at the time.
Officers had received a report of the active Goshawk nest being found abandoned in suspicious circumstances in a forest near Loch Gynack, and the programme follows experienced wildlife crime officer PC Dan Sutherland throughout his investigation.
The commentary from Dan is excellent – he speaks calmly and with authority about the link between illegal raptor persecution and gamebird shooting estates, and how the criminals have been getting away with their crimes for so long. That’s not opinion or conjecture, it’s based on factual evidence, and I applaud him for being prepared to say it on camera, knowing full well that it will attract vicious retaliation from some within the gamebird shooting industry, including, I have no doubt, official letters to his superior officers demanding punitive action against him.
Dan visits the abandoned Goshawk nest where he finds empty shotgun cartridges at the base of the tree and a shotgun wad is found lodged in the bottom of the nest.
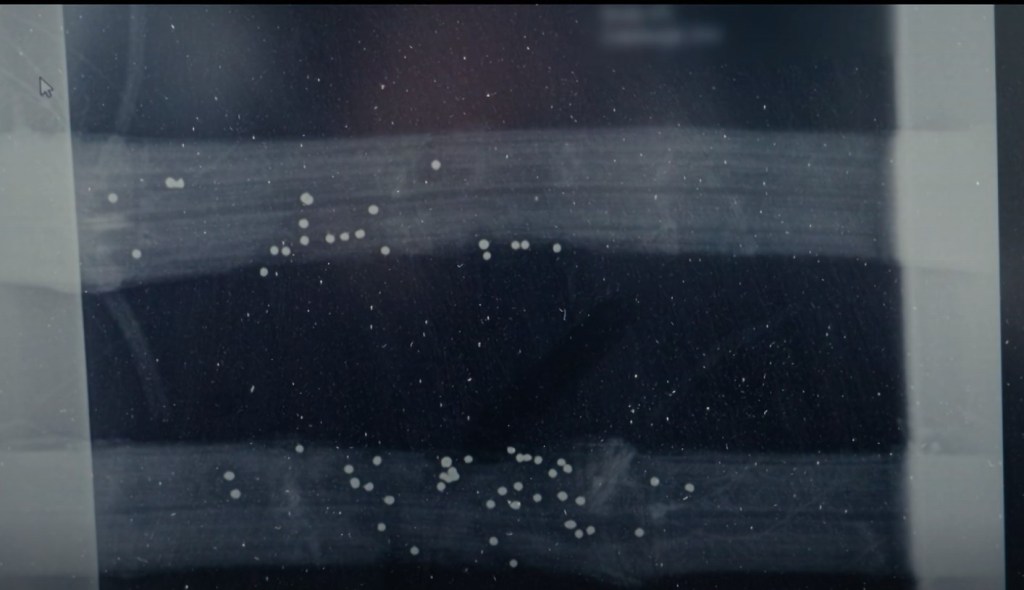
The nest is removed for forensic examination, along with several nearby tree branches. They’re taken to the Kincraig Wildlife Highland Park for x-rays, which reveal a large number of shotgun pellets:
As Dan says, the evidence is damning.
He then teams up with PC Gavin Ross from the National Wildlife Crime Unit (NWCU) and they set out to visit all the people who legally own shotguns in the area, to either rule them out of the enquiry or to see if they can provide assistance.
The first person they visit is a gamekeeper who lives on the estate. They knock at his house and a woman speaks to them through a crack in the door, telling them he’s not in. As the officers leave to go and visit the next person on their list, Dan gets a phone call from a solicitor who tells him that none of his clients will be talking to the police without him being present.
“It’s the nature of the beast”, says Dan.
Dan and Gavin comment to one another that the speed of the solicitor’s phone call is probably some kind of record – coming in less than ten minutes after they’d knocked on the gamekeeper’s door. Their wry smiles tell you this is a common occurrence and was not unexpected. It puts a halt to their investigation until they can organise a time to meet with the shotgun owners and their legal representative.

If someone had shot out a Goshawk nest on my land, potentially killing any adults or chicks present on the nest, and the police knocked on the door to see if I could assist, I’d be welcoming them in with open arms, breaking out the tea and posh biscuits and offering up all the assistance I could muster to help them find the culprit, especially if there was evidence that armed criminals had been active on my property. I certainly wouldn’t be calling in my attack dog solicitor to warn off the cops. Why would I?
At the end of the programme there’s an update on the case – the police did meet with the shotgun owners and their solicitor. The text on the screen says:
‘However, with no new leads the case has been closed‘.
I guess it was probably the usual ‘no comment’ interviews, then.
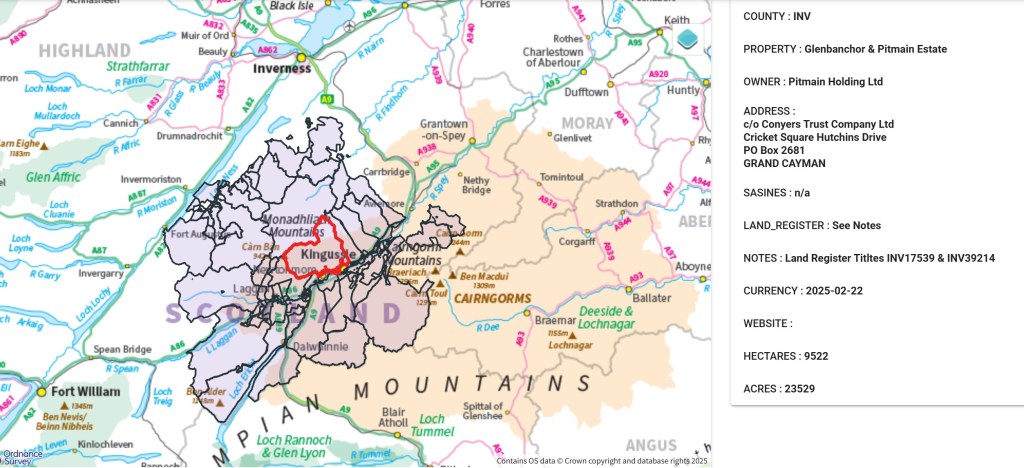
According to Andy Wightman’s excellent Who Owns Scotland website, Loch Gynack is situated on the Glenbanchor & Pitmain Estate, whose owner, Pitmain Holding Ltd, is registered in Grand Cayman:
It’s not the first time a police investigation has taken place there in relation to suspected wildlife crime. In 2019, four Greylag Geese were found poisoned at Loch Gynack – toxicology results showed they’d ingested the banned pesticide Carbofuran, so dangerous that it’s an offence to even possess this chemical in Scotland, let alone use it.
The birds had been found by estate workers who reported the incident to the police. There wasn’t any information about whether poisoned bait had been discovered and so no information about where they’d come in to contact with the Carbofuran, although given how fast-acting it is and the fact the geese were found dead together in one place, I’d think it unlikely they’d been poisoned far away.
Nobody was charged and the estate was not subject to a General Licence restriction.
Back to the Goshawk case…
The police were first notified about the abandoned Goshawk nest on 8 June 2024. This was after the enactment of the Wildlife Management & Muirburn (Scotland) Act 2024 on 30 April 2024, which introduced a licence for grouse shooting in Scotland.
I don’t know whether the Glenbanchor & Pitmain Estate applied for a grouse shooting licence in 2024. I don’t even know if they still shoot Red Grouse there (they certainly have done previously – e.g. see here and here) or whether they’ve switched to Red-legged Partridges and Pheasants as alternative quarry due to low grouse stocks, in which case they’d be exempt from needing a grouse shooting licence because the Scottish Government refused to include the shooting of RLPs and Pheasants as part of the requirement for a grouse shooting licence, despite being warned about this massive loophole.
It would be interesting to know whether (a) Pitmain Estate did apply for a grouse shooting licence in 2024, (b) if so, did NatureScot grant them a licence even though this wildlife crime investigation was ongoing, and (c) if the estate does have a five-year grouse shooting licence, will the licence be withdrawn following this incident or was the Goshawk nest beyond the area where the licence applicant indicated Red Grouse are ‘taken or shot’ (yet another loophole)?
Aside from the questions around a potential grouse shooting licence, I’ve been interested in whether NatureScot would impose a General Licence restriction following the police investigation in to the shot out Goshawk nest.
In June this year I submitted an FoI to NatureScot to ask about the status of any pending General Licence restriction decisions. My main focus was on the case concerning a Golden Eagle called ‘Merrick’ who had been shot and killed whilst she was sleeping in the Scottish Borders in October 2023.
You’ll already know that NatureScot has still not made a decision on whether to impose a General Licence restriction as a result of that crime, two years after it happened (see here).
But as well as asking about the Merrick case, I also asked how many other cases were pending.
NatureScot wrote back to me in July and said this:
You can see that the case involving the shot out Goshawk nest is included on the list (‘an incident that occurred in the Highland Council area in June 2024‘).
NatureScot says it asked Police Scotland in December 2024 for the information package NS would need to begin the process of considering whether to impose a General Licence restriction.
Seven months on, in July 2025 when NatureScot responded to my FoI, Police Scotland hadn’t provided the information to NatureScot.
The Highland Cops programme demonstrates the evidential difficulties faced by the police when investigating suspected wildlife crimes, particularly those that take place on privately-owned gamebird shooting estates, and the lengths the police will go to to find out who was responsible. It was the very reason that the Scottish Parliament introduced grouse shoot licensing as part of the Wildlife Management & Muirburn (Scotland) Act 2024.
The efforts made by PC Dan Sutherland and his colleagues were exemplary in this case. But someone, somewhere, has dropped the ball in the later stages of the enforcement process by not providing an information package in a timely manner. That’s just not good enough.
The Highland Cops episode (series 3, episode 2) is available on the BBC iPlayer here. It’s well worth an hour of your time.