Last week the RSPB published its annual UK-wide report on raptor persecution (Birdcrime 2010, see here). We said we’d comment on the report once we’d had a chance to read it. Others chose to comment on the day of its release, or to be more accurate, their commentary was probably written prior to the release and was probably based on the content of the RSPB’s press release, rather than on the actual report’s content (see here).
Birdcrime 2010 held few surprises for many of us. The report carried details of raptor persecution incidents (confirmed, probable and possible) that had been reported throughout 2010, so by not publishing the report until November 2011, many of the items could be considered ‘old news’ (or at least those incidents that had been previously reported in the media – as usual, there were several incidents recorded in this report that were not made public at the time they occurred). That’s not to say the report has no value – it is an immensely important document because it is still the only publication to collate these national statistics in one place. It would just be more useful if it could be published at the beginning of the following year to which the report relates, rather than at the end of the following year, but limited RSPB staff resources may prevent this.
One advantage of publishing the report so late is that information can be provided on the outcome of criminal proceedings for those persecution incidents that actually made it to court. For example, the report provides some previously unpublished information about the trial of gamekeeper Glenn Brown, who was found guilty in June 2011 of operating an illegal trap to take birds of prey (amongst other crimes) on Howden Moor in the Peak District in April and May 2010 (see here, here and here). According to Birdcrime 2010, Judge Caroline Goulbourn “ruled that she viewed the attack on the integrity of the RSPB investigations staff by Bertie Woodcock QC on behalf of Knights Solicitors as an aggravating factor in the case. In addition, she criticised Brown’s employer, Geoff Eyre, who leases Howden Moor from the National Trust, for being evasive and reluctant to answer questions” [Birdcrime 2010, p.17].
Incidentally, there is further detail about this case that has been written in the RSPB’s newsletter, Legal Eagle 65. On page 2 the following has been written: “During the ten day trial, the prosecution relied on expert evidence including Prof Ian Newton, Dr Mick Marquiss, Stewart Scull, Dr Alisdair Wood and Guda van der Burght. The defence case, led by Bertie Woodcock QC, centred on the fact that Brown was not using the trap and the entire investigation was a set up with RSPB officers acting in bad faith throughout”. It’s good to see that Judge Goulbourn ruled against this, although what will happen at Brown’s impending appeal remains to be seen. Legal Eagle 65 reports that this appeal “is expected to take place in 2012”.
In addition to the case studies of earlier persecution incidents, Birdcrime 2010 reports that annual poisoning figures were down from 2009 (128 reported poisoning incidents in 2010, compared to 153 in 2009). It also reports that the 2010 figure is below the average for the last five years (2005-2009 average of 150 incidents). Unsurprisingly, it is this aspect that has been picked up on by the game-shooting lobby (e.g. see here). There has also been much made in the media this year about the ‘low’ poisoning figures for 2011 (e.g. see here) – although the published figures only relate to the first half of 2011; figures from June 2011 onwards are not yet available. So is this a sign of progress, as many of the game-shooting lobby would have us believe, or is it indicative of something else? For example, the lower figures could well be an indication that the gamekeepers have finally seen the light and have decreased their poisoning efforts. On the other hand, it could be an indication that gamekeepers are either (a) getting better at hiding their crimes, (b) switching to other persecution methods such as shooting, which is less likely to be detected, or (c) reporting efforts by the authorities have fallen. At this point I don’t think that either ‘side’ can claim a ‘victory’ in the on-going war of words. It is far too early to tell. For example, if you look at the graph that was published in the RSPB’s earlier report, The Illegal Killing of Birds of Prey in Scotland in 2010 (see here), then this reported decline in poisoning incidents can be seen in much clearer context. The graph I’m referring to appears on page 11 of that report and shows the number of confirmed poisoning incidents in Scotland from 1989-2010. The graph has been recreated for this post – see below (thanks to the contributor who sent it!).
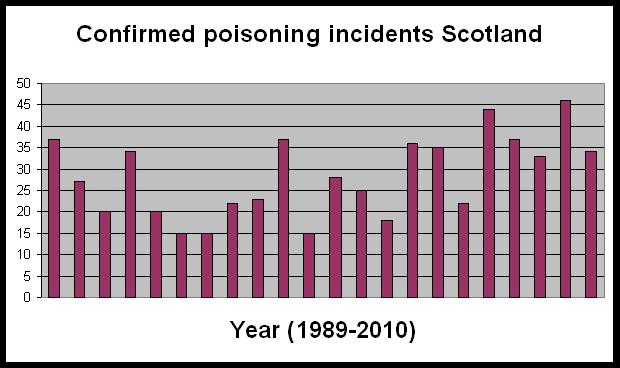 If you look closely at the graph, you will see a great deal of variation between years in the number of confirmed poisoning incidents. Of particular interest are the years 1994 and 1995 – in these two years, confirmed poisoning incidents dropped to a low of 15 from a previous high of 35+. However, if you then look at the following three years, the number of confirmed incidents steadily rose until they reached 35+ again. In 1999, the figure dropped again to 15, and from then until 2010, that figure has steadily risen and fallen, although never reaching the low of 15 again. So what does that tell us? I’m fairly sure that in the years 1994 and 1995, the game shooting lobby would have declared a ‘victory’ as the figures had dropped so much, and would have shouted from the hilltops that they’d changed their ways. I’m also fairly sure that in the following three years when the figures rose again, the conservationists would have declared a ‘victory’ and pronounced that their claims of widespread persecution had been vindicated. Either way, it is clear that neither ‘side’ can draw conclusions just based on an annual figure; for a trend to be detected, we need to see long-term figures.
If you look closely at the graph, you will see a great deal of variation between years in the number of confirmed poisoning incidents. Of particular interest are the years 1994 and 1995 – in these two years, confirmed poisoning incidents dropped to a low of 15 from a previous high of 35+. However, if you then look at the following three years, the number of confirmed incidents steadily rose until they reached 35+ again. In 1999, the figure dropped again to 15, and from then until 2010, that figure has steadily risen and fallen, although never reaching the low of 15 again. So what does that tell us? I’m fairly sure that in the years 1994 and 1995, the game shooting lobby would have declared a ‘victory’ as the figures had dropped so much, and would have shouted from the hilltops that they’d changed their ways. I’m also fairly sure that in the following three years when the figures rose again, the conservationists would have declared a ‘victory’ and pronounced that their claims of widespread persecution had been vindicated. Either way, it is clear that neither ‘side’ can draw conclusions just based on an annual figure; for a trend to be detected, we need to see long-term figures.
But do these figures actually provide the full picture? If you read the recent paper on historical persecution at Atholl Estate (see here), then it’s pretty obvious that the ‘official’ persecution figures are meaningless, in the sense that they don’t tell the whole story. And from a conservation perspective, the figures, whether accurate or not, are not really that important. To steal a line from the recent paper on peregrine persecution on grouse moors (see here), “….it is the population level impact that is important, rather than the number of confirmed persecution cases”. We now have peer-reviewed scientific studies that have shown how persecution on grouse moors is having a population level impact on several vulnerable species (golden eagle, hen harrier, red kite and now peregrine). We have yet to see any peer-reviewed scientific studies that can counter these findings and show that these species are NOT impacted by persecution on grouse moors at a population scale. Why do you think that is, and more to the point, what are our politicians going to do about the published findings, apart from telling us that the Scottish government’s support for grouse shooting “goes beyond words“? (see here). Let’s hope that support doesn’t go beyond action as well.

 Meanwhile, back in the real world, an article in the Wicklow People yesterday says that a red kite and a buzzard have been found poisoned in County Wicklow, Ireland.
Meanwhile, back in the real world, an article in the Wicklow People yesterday says that a red kite and a buzzard have been found poisoned in County Wicklow, Ireland.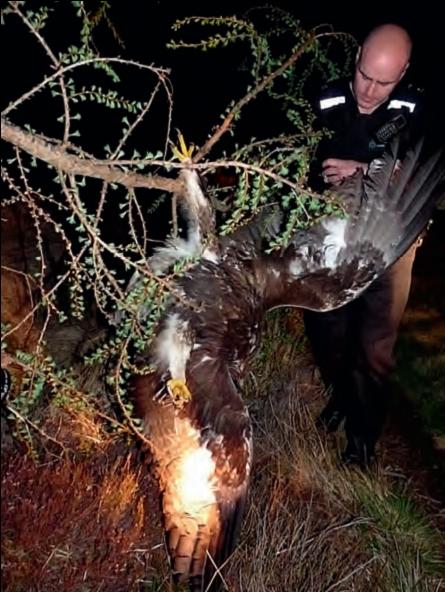 The RSPB has published its annual report on raptor persecution in the UK (Birdcrime 2010). Poisoning reports are down (128 reported in 2010; 153 reported in 2009). Birds confirmed poisoned in 2010 include:
The RSPB has published its annual report on raptor persecution in the UK (Birdcrime 2010). Poisoning reports are down (128 reported in 2010; 153 reported in 2009). Birds confirmed poisoned in 2010 include: Glen Esk is, of course, where golden eagle ‘Alma’ was found poisoned two years ago (see
Glen Esk is, of course, where golden eagle ‘Alma’ was found poisoned two years ago (see  Well finally, on behalf of the Scottish Government, SASA (Science and Advice for Scottish Agriculture) has published the poisoning figures from the second quarter of 2011 (covering the period from April to June), and guess what? More raptors were illegally poisoned during this period. Seems a bit of a coincidence that these figures have been published four months late and on the very day that people were encouraged to make a Freedom of Information request to SASA to obtain the 2011 poisoning data. Nevertheless, the publication of these data is still welcome and provides us with cold hard facts about the continuing illegal poisoning of our native species.
Well finally, on behalf of the Scottish Government, SASA (Science and Advice for Scottish Agriculture) has published the poisoning figures from the second quarter of 2011 (covering the period from April to June), and guess what? More raptors were illegally poisoned during this period. Seems a bit of a coincidence that these figures have been published four months late and on the very day that people were encouraged to make a Freedom of Information request to SASA to obtain the 2011 poisoning data. Nevertheless, the publication of these data is still welcome and provides us with cold hard facts about the continuing illegal poisoning of our native species. Millden Estate near Brechin, Angus has been put up for sale with a whopping £17.5 million price tag. If the estate is sold as a whole (as opposed to up to 13 Lots), it will become the most expensive Scottish country estate ever sold on the open market, according to Scotland on Sunday.
Millden Estate near Brechin, Angus has been put up for sale with a whopping £17.5 million price tag. If the estate is sold as a whole (as opposed to up to 13 Lots), it will become the most expensive Scottish country estate ever sold on the open market, according to Scotland on Sunday.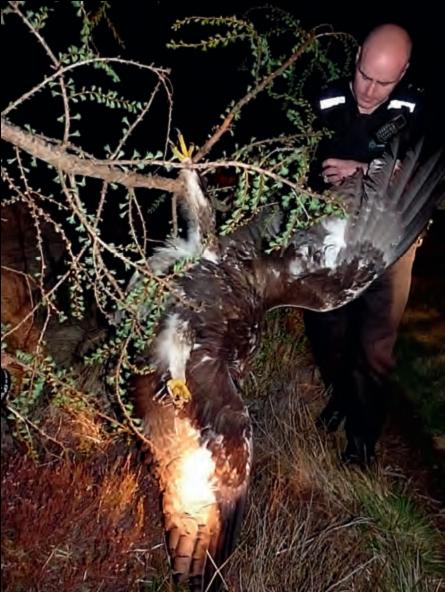 The RSPB has just published its annual report on raptor persecution in Scotland. The report, ‘The Illegal Killing of Birds of Prey in Scotland 2010‘ is the only known published record of all known persecution incidents including poisoning, shooting and trapping, in contrast to the PAW Scotland annual report which only details poisoning incidents. As well as the confirmed incidents of persecution, the report also provides information about ‘probable’ incidents (those where the available evidence points to illegality as by far the most likely explanation but where the proof of an offence is not categorical) and ‘possible’ incidents (where an illegal act is a possible explanation but where another explanation would also fit the known facts).
The RSPB has just published its annual report on raptor persecution in Scotland. The report, ‘The Illegal Killing of Birds of Prey in Scotland 2010‘ is the only known published record of all known persecution incidents including poisoning, shooting and trapping, in contrast to the PAW Scotland annual report which only details poisoning incidents. As well as the confirmed incidents of persecution, the report also provides information about ‘probable’ incidents (those where the available evidence points to illegality as by far the most likely explanation but where the proof of an offence is not categorical) and ‘possible’ incidents (where an illegal act is a possible explanation but where another explanation would also fit the known facts).