This is the third blog in our series about the 2013 Scottish Police Wildlife Crime conference. (NB: these are not being produced in the order the presentations were made at the conference). Here’s what Duncan Orr-Ewing of RSPB Scotland had to say on the topic of raptor persecution:
“Good morning everybody, I think most of you know me here, but my name is Duncan Orr-Ewing, I’m Head of Species and Land Management at RSPB Scotland, based in Edinburgh. My talk today, what I plan to do is give a bit of an outline of the issue if you like, then cover some of the sort of on-going work that is underway to try and address the problems, and then take a bit of a forward view if you like, on what the next steps might be. I should probably also confess at this point that I’m also a Director of the Langholm Demonstration Project, which Simon’s just talked about. I’m not planning to talk a lot about that but obviously as a science-based organisation the RSPB is heavily involved with that and a range of other scientific projects to try and identify solutions to some of the issues on-going in this area. I should also say, just briefly at the outset, as a science-based organisation our focus is on the conservation of raptors, we’re informed by the science, our focus is on raptor populations. We are not opposed to hunting as an organisation provided it’s carried out sustainably and legally.
Taking us back to the beginning, I think the advent of the Scottish Parliament has seen political unity break out on this issue, and I’m minded to remind you all of Donald Dewar’s statement that the persecution of birds of prey in Scotland is a national disgrace, and subsequent Environment Ministers of all political persuasions that we’ve had in power in Scotland have also pretty well taken this sort of line. This is not a political issue, this is a significant conservation issue. The RSPB is involved with this because it is a conservation issue and we’re rightly standing up for the interests of raptors. And I would also remind you at this stage that there are no enlightened countries, shall we say, in the world, that I think I can point to, where people are allowed to illegally, or, in most cases I would also say, legally kill raptors. They’re rightly protected as I’ll come on to say.
So just talking about some of the issues, this is the Skibo Estate in Sutherland taking you back a few years, in the foreground you’ll see one of three golden eagles that were found poisoned on that estate. Why should we be concerned about this? This incident, in itself, has probably resulted in a set-back for that local golden eagle population for many many years to come, that one incident. So the question we ask ourselves here is, why has this been allowed to happen? The individuals that have been involved with this, why are they involved with the hunting industry? Why haven’t they been removed by the hunting industry? Why haven’t they been marginalised? Instead, we see some of these people held up as exemplars of best practice, in particularly in the grouse moor industry, and that is very disappointing and I think that has to be addressed.
I’ll also remind you that raptors are not just important as the Minister said, on their own volition, in their own right, they’re also important because they’re important to local economies. Need I say the story of the sea eagle, a reintroduced species, its value to the local Mull economy – £5 million per annum. People come to Scotland to see our environment, they’re attracted to seeing some of these iconic species that we have here, the sea eagle is one of those.
Another example, and there are examples across the whole of Scotland, the length and breadth of Scotland, the Galloway Kite Trail, also bringing in hundreds of thousands of pounds a year to a local Dumfries & Galloway economy. And some of these benefits that come from raptor conservation, supported it has to be said by local estates and enlightened land owners, they are now very important to the economies of some of our most rural areas in Scotland.
So why are raptors protected? And this is a very fundamental point which informs very much how we think about this issue. Firstly, they’re long-lived birds with slow reproductive rates, so illegal killing can be highly detrimental to their populations. Scotland also has a particularly poor history in conserving our raptor species. We have had national extinctions, I mean even birds like the buzzards, because of what we did two centuries ago, were driven to the edge of what should be their former range and only now are some of these species recovering their populations, and indeed, some have had to be reintroduced by humans with the support of local land owners because they were driven to extinction, and the red kite and the sea eagle being those. And we still, I’m afraid, based on some of this history, still have a prejudice in the UK and Scotland towards predators, and this isn’t just raptors, this is all sorts of predators, you know, big cats, wild cats, pine martens, otters, badgers, there is prejudice against these species as well, which persists in some places.
So I want to touch now just on what the impact of illegal killing has on three raptor species and I’m taking the golden eagle, hen harrier and red kite as examples, and we now have a very good body of science to support these assertions.
 So I’m referring here to the SNH Golden Eagle Framework, and here the red areas that are on the map show the areas in Scotland where the golden eagle population is considered to be in unfavourable conservation status. And overlaid on that map are the incidents of illegal persecution, poisoning incidents, between 2006 and 2012. And you’ll see there’s a strong coincidence with illegal persecution of golden eagle poisoning in this case and where the bird is in unfavourable conservation status. And in 2012 alone, I’ll just highlight three cases of crime against golden eagles that were detected: one in the far north west of Scotland, one in the Angus area and the other in Dumfries & Galloway/Strathclyde border. And every time one of these cases happens, I would say, you know, the trust that should be there between land managers and conservationists takes a step back.
So I’m referring here to the SNH Golden Eagle Framework, and here the red areas that are on the map show the areas in Scotland where the golden eagle population is considered to be in unfavourable conservation status. And overlaid on that map are the incidents of illegal persecution, poisoning incidents, between 2006 and 2012. And you’ll see there’s a strong coincidence with illegal persecution of golden eagle poisoning in this case and where the bird is in unfavourable conservation status. And in 2012 alone, I’ll just highlight three cases of crime against golden eagles that were detected: one in the far north west of Scotland, one in the Angus area and the other in Dumfries & Galloway/Strathclyde border. And every time one of these cases happens, I would say, you know, the trust that should be there between land managers and conservationists takes a step back.
With hen harrier I take you back to 2000 and a case in Strathspey in Morayshire, and here was a case of a gamekeeper shooting a hen harrier at the nest, successfully convicted for this, and I’m afraid that this was the first successful conviction of a gamekeeper for killing a hen harrier, although this is considered to be widespread practice, and I’ve put this in really just to show how difficult it is to secure convictions in this kind of case because these cases occur in remote areas, in this case on a grouse moor, you know, far away from public roads, it is difficult to get access and bring these people to justice but in this case we were successful in doing that and subsequently there have also been a couple of other successful convictions. But we think this is still widespread practice, and following on from the Joint Raptor Study than Simon mentioned earlier, we do know that that resulted in an escalation of crime against hen harriers because people saw that hen harriers were blamed for suppressing grouse populations and as a result people saw justification for taking the law into their own hands. And in 2010, as a result of this, we’ve just carried out a national population survey with the Raptor Study Groups and others, into hen harriers, we have a national population decline of 20% in hen harriers. And if I tell you that on grouse moors, driven grouse moors in the UK, we only have five breeding pairs of hen harriers, and as many of you will know the hen harrier is on the verge of extinction in England as a result of human persecution. Other work that has been done by people in this room actually and GWCT and others has shown that there is room for 500 breeding pairs of hen harriers on driven grouse moors in the UK, so their population is being suppressed and they are at very low levels. And I’ve just put this in to show that this is a species that isn’t affected really by illegal poisoning – most of the impacts on hen harriers are either by direct nest destruction, or in this case, illegal trapping. You can see a male hen harrier there, caught in a leg-hold trap.
 And red kite, a species which I have a fair bit of involvement with myself, again we’re in a unique situation here where we have an almost totally marked population of birds, because the bird was reintroduced, all the birds that were released were wing-tagged and we know the fate of these birds because we’ve been radio-tracking them and recording all the wing tag data. And we’re also in a position where we’re able to compare between two reintroduction areas so in the south of England, in the Chilterns, there was a similar reintroduction and we released the same number of birds, about 90 birds were released, also 90 birds in north Scotland and the population in 2006 of red kites in the Chilterns area, with similar productivity, same number of young produced compared roughly to north Scotland is over 300 pairs whereas in north Scotland the population has bubbled along and has stayed pretty well static at about 50 breeding pairs. Indeed the Chilterns population this year is nearly 1,000 breeding pairs whereas the north Scotland population is still stuck below 60 breeding pairs. And the main difference between these rates of growth is explained by the prevailing levels of illegal poisoning in the two countries, i.e. we have far higher levels of illegal poisoning. And last time I was here speaking to you was about red kites and I reported that since reintroduction we’d found 50 kites that had been confirmed as being illegally poisoned since reintroduction began in 1989 and that figure is now 75 in Scotland. And where is this happening? There is a strong coincidence, illegal activity in the east of Scotland in the areas shaded, which are grouse moors, hence the work we’re doing at Langholm and elsewhere to try and find some solutions to this problem. And increasingly it is looking like the driven grouse moor areas are the problem areas to focus on.
And red kite, a species which I have a fair bit of involvement with myself, again we’re in a unique situation here where we have an almost totally marked population of birds, because the bird was reintroduced, all the birds that were released were wing-tagged and we know the fate of these birds because we’ve been radio-tracking them and recording all the wing tag data. And we’re also in a position where we’re able to compare between two reintroduction areas so in the south of England, in the Chilterns, there was a similar reintroduction and we released the same number of birds, about 90 birds were released, also 90 birds in north Scotland and the population in 2006 of red kites in the Chilterns area, with similar productivity, same number of young produced compared roughly to north Scotland is over 300 pairs whereas in north Scotland the population has bubbled along and has stayed pretty well static at about 50 breeding pairs. Indeed the Chilterns population this year is nearly 1,000 breeding pairs whereas the north Scotland population is still stuck below 60 breeding pairs. And the main difference between these rates of growth is explained by the prevailing levels of illegal poisoning in the two countries, i.e. we have far higher levels of illegal poisoning. And last time I was here speaking to you was about red kites and I reported that since reintroduction we’d found 50 kites that had been confirmed as being illegally poisoned since reintroduction began in 1989 and that figure is now 75 in Scotland. And where is this happening? There is a strong coincidence, illegal activity in the east of Scotland in the areas shaded, which are grouse moors, hence the work we’re doing at Langholm and elsewhere to try and find some solutions to this problem. And increasingly it is looking like the driven grouse moor areas are the problem areas to focus on.
The big concern if you like with the driven grouse shooting set-up these days is that this sport seems to be moving into a new, more intensive phase. So over the past 10-15 years we’ve seen land management systems that have been employed for England for quite a number of years, coming up to Scotland, means more intensive management, more keepers, more predator control, killing as you’re aware of hares and deer tick hosts, increased burning, and we’ve mapped this and we know that there is a strong coincidence where this intensive management is coming in there is a prevalence also of illegal raptor persecution. And I would see this very much as the problem area to focus on in the forthcoming years. There have been some very notorious cases of course, that have occurred in these places where this intensification of management has taken place, in this case ‘Alma’, a golden eagle being radio-tracked and being found dead in the Angus glens a few years ago, illegally poisoned.
So is the situation improving? I think the answer is yes in some places, and this is a map of BTO data on the breeding bird survey buzzard trend, and you will see that the buzzard population, as many of you will know, has increased quite rapidly in recent years but now it’s plateau-ed off as you’d expect and we have a largely stable buzzard population but this species is still absent from some areas of its former range but I think the next breeding bird atlas, coordinated by BTO, will show that the buzzard has recovered large areas of its former range, which is good progress.
Earlier today we were talking about the illegal poisoning incidents in Scotland. This is a bar chart showing the number of reported poisoning incidents over the years since 1989, and as the Minister mentioned, over the past couple of years we have seen a significant decline in illegal poisoning and that is again very good progress. We would say this is informed by a few things perhaps as background which have helped us get to where we are today and this is work in progress, there’s no room for complacency here and we will work with Scottish Land and Estates and others to make sure that we continue to bear down on this problem.
 But the high point [on the graph] in 2009 was when Alma, the eagle that I mentioned earlier, was found poisoned. We also had a case, the Skibo case also mentioned earlier, a seizure of 10kg of Carbofuran, one of the poisons most implicated in illegal poisoning. And then again, 2011, another satellite-tagged eagle found poisoned. And of course the introduction of vicarious liability making land owners more responsible for the actions of their employees. These welcome steps, apart from the poisonings of course, are helping to move the situation onwards but as I say, we’re not complacent and we will continue to work with partners in the Partnership Against Wildlife Crime to bear down on this problem. What we’ve learned through poisoning hopefully will transfer to other types of raptor crime in due course.
But the high point [on the graph] in 2009 was when Alma, the eagle that I mentioned earlier, was found poisoned. We also had a case, the Skibo case also mentioned earlier, a seizure of 10kg of Carbofuran, one of the poisons most implicated in illegal poisoning. And then again, 2011, another satellite-tagged eagle found poisoned. And of course the introduction of vicarious liability making land owners more responsible for the actions of their employees. These welcome steps, apart from the poisonings of course, are helping to move the situation onwards but as I say, we’re not complacent and we will continue to work with partners in the Partnership Against Wildlife Crime to bear down on this problem. What we’ve learned through poisoning hopefully will transfer to other types of raptor crime in due course.
Ok, this is just to remind you also that there are quite a large number of birds that have been killed since 1989 through illegal poisoning – 930 birds and animals have been discovered poisoned and hopefully in the future we can make a dent in that situation. Ultimately, consign illegal poisoning to history, that’s what we want to do.
But also worth mentioning that birds of prey are killed in other ways, they’re shot, trapped or have their nests destroyed and we need to start progressing that as well, as was stated earlier.
So what are the solutions? As we’ve heard earlier, we’re developing legal alternatives to killing birds of prey, and diversionary feeding is one such method, which in the case of the hen harrier has been shown to be pretty effective and we hope over the next few years the grouse moor sector will start adopting this technique and rolling it out across driven grouse moors across Scotland and perhaps even in the north of England. These are legal techniques to solve problems.
I think we also need a model of how grouse moors can be managed more sustainably. It’s not acceptable that this continued intensification occurs and the people that are involved with it are held up as exemplars of best practice if that involves illegal activity. We need a model that fits more with 21st century public expectations and is not predicated on ever-increasing grouse bags. Some of the moors which we see now have the highest grouse bags they’ve had for many years. You would think there would be room for raptors there. They also don’t have the grouse cycle that they used to have because we have medicated grit and other methods developed by GWCT to prevent that from happening. So why can’t these places tolerate raptors? Many of the grouse moors that we’re talking about here don’t have any breeding raptors, let alone hen harriers and eagles, they are black holes for raptors. But we also need more land owners and their employees to work with the police and marginalise those who undermine other good practice and that is happening to a large extent now, through PAW and the work of Scottish Land and Estates and others and we very much welcome that.
And of course there has to be a deterrent out there and that includes effectively robust policing, enforcement, to deal with those serious incidents when they occur.
And I throw this open, but do we need more regulation of the sporting industry? It was discussed last time, the Wildlife and Natural Environment (WANE) Act went through the Scottish Parliament. We have one of the most unregulated shooting industry anywhere in the world. Does this contribute to this problem? In Germany, North America, Scandinavia, other countries, they have quite an established system of regulation for hunting.
But what it’s all about for us, and we will measure success of all of these actions, is through improved populations of the key species, in this case goshawks, ospreys, hen harriers. That is how we will measure progress. But this will be delivered through a range of partnership arrangements as well. It’s easy to knock these partnership arrangements but they are important. They build trust, they build dialogue and in Scotland as a small country of only 5 million people we have good communication between most of the key players here, and that can only help us move this along.
I’m delighted that Scottish Land and Estates are developing their Wildlife Estates initiative; some RSPB staff are involved with helping develop this and we will help Scottish Land and Estates encourage those good land owners who want to do the right thing as we move forward with that programme.
The Langholm Demonstration Project, I won’t dwell on that in detail because Simon’s covered a lot of it – a very important project. This is the model for sustainable grouse moor management going forward. Many of you may not see that, and Simon said, it’s not without problems, the project, but we’re working our way through those problems as partners, and this less intensive approach to grouse moor management, within the law, with protected raptor species, has to be the way forward, and a combination of hunting and conservation occurs.
And of course I should mention the Partnership Against Wildlife Crime, which over the past few years has really developed into a solid partnership and we’re all working together in the same direction. Thank you very much”.

 Joan McAlpine: As the minister acknowledged, there have been a number of shocking incidents across Scotland during the past year. Earlier this month, a golden eagle was shot on the southern upland way. In light of that, will the minister reassure the Parliament that investigations into the illegal killing of eagles are carried out quickly and effectively? Is he willing to update the Parliament on the investigation into the killing of the golden eagle that was found on Deeside in May 2012?
Joan McAlpine: As the minister acknowledged, there have been a number of shocking incidents across Scotland during the past year. Earlier this month, a golden eagle was shot on the southern upland way. In light of that, will the minister reassure the Parliament that investigations into the illegal killing of eagles are carried out quickly and effectively? Is he willing to update the Parliament on the investigation into the killing of the golden eagle that was found on Deeside in May 2012? There’s an article in the Scotsman today about Scottish gamekeepers offering to help the fire service put out fires, started by, er,…well it depends on whose opinion you accept.
There’s an article in the Scotsman today about Scottish gamekeepers offering to help the fire service put out fires, started by, er,…well it depends on whose opinion you accept. An article in the Scotsman today suggests that the recent death of the shot golden eagle (see
An article in the Scotsman today suggests that the recent death of the shot golden eagle (see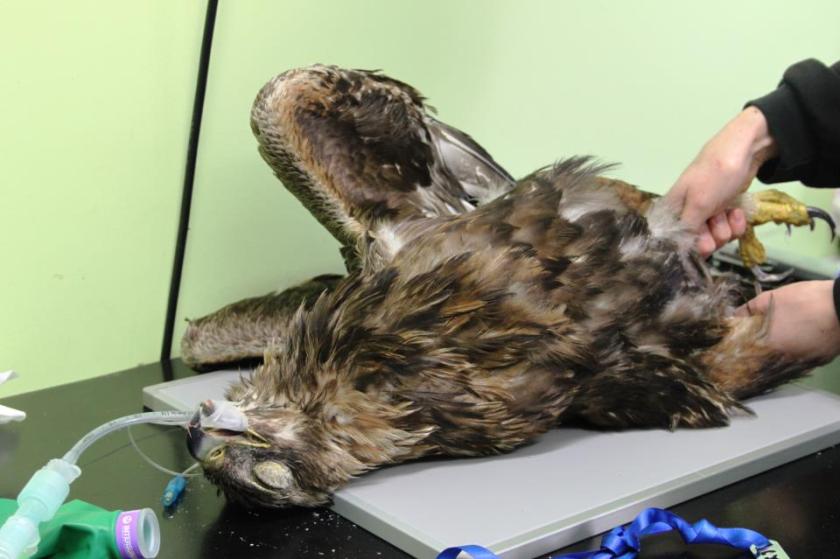 
 So I’m referring here to the SNH Golden Eagle Framework, and here the red areas that are on the map show the areas in Scotland where the golden eagle population is considered to be in unfavourable conservation status. And overlaid on that map are the incidents of illegal persecution, poisoning incidents, between 2006 and 2012. And you’ll see there’s a strong coincidence with illegal persecution of golden eagle poisoning in this case and where the bird is in unfavourable conservation status. And in 2012 alone, I’ll just highlight three cases of crime against golden eagles that were detected: one in the far north west of Scotland, one in the Angus area and the other in Dumfries & Galloway/Strathclyde border. And every time one of these cases happens, I would say, you know, the trust that should be there between land managers and conservationists takes a step back.
So I’m referring here to the SNH Golden Eagle Framework, and here the red areas that are on the map show the areas in Scotland where the golden eagle population is considered to be in unfavourable conservation status. And overlaid on that map are the incidents of illegal persecution, poisoning incidents, between 2006 and 2012. And you’ll see there’s a strong coincidence with illegal persecution of golden eagle poisoning in this case and where the bird is in unfavourable conservation status. And in 2012 alone, I’ll just highlight three cases of crime against golden eagles that were detected: one in the far north west of Scotland, one in the Angus area and the other in Dumfries & Galloway/Strathclyde border. And every time one of these cases happens, I would say, you know, the trust that should be there between land managers and conservationists takes a step back. And red kite, a species which I have a fair bit of involvement with myself, again we’re in a unique situation here where we have an almost totally marked population of birds, because the bird was reintroduced, all the birds that were released were wing-tagged and we know the fate of these birds because we’ve been radio-tracking them and recording all the wing tag data. And we’re also in a position where we’re able to compare between two reintroduction areas so in the south of England, in the Chilterns, there was a similar reintroduction and we released the same number of birds, about 90 birds were released, also 90 birds in north Scotland and the population in 2006 of red kites in the Chilterns area, with similar productivity, same number of young produced compared roughly to north Scotland is over 300 pairs whereas in north Scotland the population has bubbled along and has stayed pretty well static at about 50 breeding pairs. Indeed the Chilterns population this year is nearly 1,000 breeding pairs whereas the north Scotland population is still stuck below 60 breeding pairs. And the main difference between these rates of growth is explained by the prevailing levels of illegal poisoning in the two countries, i.e. we have far higher levels of illegal poisoning. And last time I was here speaking to you was about red kites and I reported that since reintroduction we’d found 50 kites that had been confirmed as being illegally poisoned since reintroduction began in 1989 and that figure is now 75 in Scotland. And where is this happening? There is a strong coincidence, illegal activity in the east of Scotland in the areas shaded, which are grouse moors, hence the work we’re doing at Langholm and elsewhere to try and find some solutions to this problem. And increasingly it is looking like the driven grouse moor areas are the problem areas to focus on.
And red kite, a species which I have a fair bit of involvement with myself, again we’re in a unique situation here where we have an almost totally marked population of birds, because the bird was reintroduced, all the birds that were released were wing-tagged and we know the fate of these birds because we’ve been radio-tracking them and recording all the wing tag data. And we’re also in a position where we’re able to compare between two reintroduction areas so in the south of England, in the Chilterns, there was a similar reintroduction and we released the same number of birds, about 90 birds were released, also 90 birds in north Scotland and the population in 2006 of red kites in the Chilterns area, with similar productivity, same number of young produced compared roughly to north Scotland is over 300 pairs whereas in north Scotland the population has bubbled along and has stayed pretty well static at about 50 breeding pairs. Indeed the Chilterns population this year is nearly 1,000 breeding pairs whereas the north Scotland population is still stuck below 60 breeding pairs. And the main difference between these rates of growth is explained by the prevailing levels of illegal poisoning in the two countries, i.e. we have far higher levels of illegal poisoning. And last time I was here speaking to you was about red kites and I reported that since reintroduction we’d found 50 kites that had been confirmed as being illegally poisoned since reintroduction began in 1989 and that figure is now 75 in Scotland. And where is this happening? There is a strong coincidence, illegal activity in the east of Scotland in the areas shaded, which are grouse moors, hence the work we’re doing at Langholm and elsewhere to try and find some solutions to this problem. And increasingly it is looking like the driven grouse moor areas are the problem areas to focus on. But the high point [on the graph] in 2009 was when Alma, the eagle that I mentioned earlier, was found poisoned. We also had a case, the Skibo case also mentioned earlier, a seizure of 10kg of Carbofuran, one of the poisons most implicated in illegal poisoning. And then again, 2011, another satellite-tagged eagle found poisoned. And of course the introduction of vicarious liability making land owners more responsible for the actions of their employees. These welcome steps, apart from the poisonings of course, are helping to move the situation onwards but as I say, we’re not complacent and we will continue to work with partners in the Partnership Against Wildlife Crime to bear down on this problem. What we’ve learned through poisoning hopefully will transfer to other types of raptor crime in due course.
But the high point [on the graph] in 2009 was when Alma, the eagle that I mentioned earlier, was found poisoned. We also had a case, the Skibo case also mentioned earlier, a seizure of 10kg of Carbofuran, one of the poisons most implicated in illegal poisoning. And then again, 2011, another satellite-tagged eagle found poisoned. And of course the introduction of vicarious liability making land owners more responsible for the actions of their employees. These welcome steps, apart from the poisonings of course, are helping to move the situation onwards but as I say, we’re not complacent and we will continue to work with partners in the Partnership Against Wildlife Crime to bear down on this problem. What we’ve learned through poisoning hopefully will transfer to other types of raptor crime in due course. 2013 is the Year of Natural Scotland – a Scottish Government initiative aimed at getting people out and about to enjoy Scotland’s natural wonders (see
2013 is the Year of Natural Scotland – a Scottish Government initiative aimed at getting people out and about to enjoy Scotland’s natural wonders (see