Just how stupid/arrogant do you have to be to go on record saying, “Clearly, any illegal [hen harrier] persecution is not happening“, when it so demonstrably is?!
This is what Mark Cunliffe-Lister, Chair of the grouse moor owners’ lobby group, the Moorland Association, told BBC Radio 4’s Farming Today programme this morning.
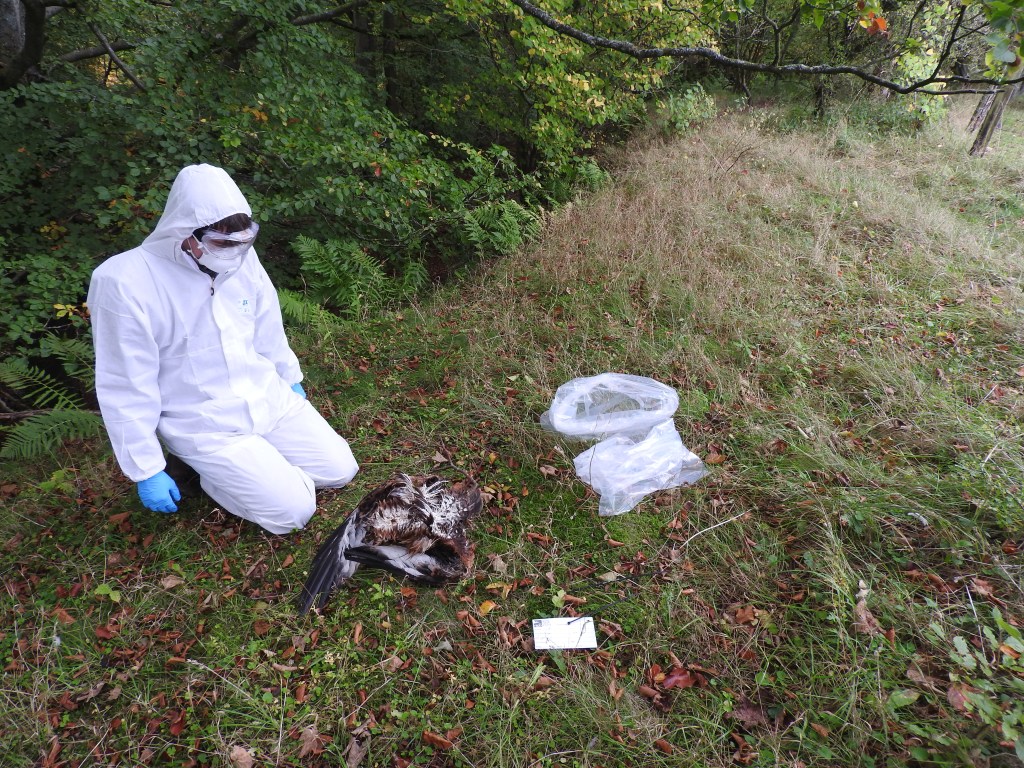
It’s an astonishing claim to make when the evidence to refute such a claim is so readily available, and even more so on the day when we learned that at least 101 hen harriers have now gone ‘missing’ / been illegally killed since 2018 (see here).
Although Cunliffe-Lister does have a history of ‘forgetting’ to mention things when it comes to hen harrier persecution (see here). Oh, and he also forgot to mention this morning the poisoned red kite that was discovered on his estate (Swinton) in 2021 – the one that North Yorkshire Police refused to investigate (see here).
When Cunliffe-Lister was called out on his claim by the interviewer Caz Graham, he had the brass neck to argue that there “do seem to be isolated incidents“. Does he think that 101 missing/killed hen harriers are ‘isolated incidents’?? Oh, and some of those 101 include brood meddled hen harriers.
Also interviewed on this morning’s programme was John Holmes, Director of Strategy at Natural England and who oversees the hen harrier brood meddling sham. Holmes was questioned at length about Wild Justice’s criticisms of the hen harrier brood meddling sham, including the unimpressive scientific approach to the trial. Holmes argued that Natural England was being advised by an independent panel of ornithologists and statisticians. What he didn’t say, as Mark Avery pointed out on Twitter, is that the identities of those ornithologists and statisticians is being kept a secret, as is their scientific advice.
Holmes also argued that Natural England has ‘expert social scientists’ to examine whether brood meddling has changed the opinion of grouse moor owners and managers towards hen harriers. NE don’t need ‘expert social scientists’ to find an answer, the illegal persecution statistics tell us all we need to know.
The interview is available on BBC iPlayer for the next 29 days (here, starts at 4.59 mins) but I’ve produced a transcript for posterity:
Presenter Caz Graham: Hen harriers are beautiful birds that live in the uplands across the UK but their numbers are precariously low, particularly in England.
These low numbers are blamed on predation and on persecution by gamekeepers who illegally target birds of prey because they feed on grouse eggs and chicks. Most hen harrier nests in England are on land managed as grouse moor.
To try and rebuild the population a Government-led Hen Harrier Recovery Plan began in 2016. One element of it is a trial of what’s called ‘brood management’, where eggs and chicks are taken from hen harrier nests, raised in captivity and re-released later back in to the wild so their parents take fewer grouse chicks to feed them.
The Moorland Association, one of several partners in the brood management trial say that this year has been a real success with 24 chicks released. The population of hen harriers in England is now at the highest it’s been for 100 years, they say.
The wildlife campaign group Wild Justice welcomes the increase in hen harrier numbers but is critical of brood management. I put some of their points to Mark Cunliffe-Lister, the Chair of the Moorland Association who first gave me his response to these latest figures.
Chair of Moorland Association Mark Cunliffe-Lister: It’s been a fantastic success, we’ve shown that as a dedicated team we can take the chicks from the nest, we can breed them in captivity, we can re-release them on another site and they can live a perfectly good wild life going forwards.
Caz Graham: How have the birds that have been reared this way in previous years fared? Presumably they’re all tagged, they’re all tracked, you know how they’re doing?
Mark Cunliffe-Lister: Yep, no, absolutely. So, I mean like everything in the wild, they look around for different territories, they move about. I think one of the interesting things has been when we release them is they’re not necessarily, quite a lot of hen harriers will come back to exactly where they were born and bred, these ones will look around for other territories so that’s been very successful as they’ve taken on different territories and gone to different areas.
Caz Graham: Have they bred themselves?
Mark Cunliffe-Lister: Yes, they’ve bred themselves as well so they’ve shown breeding technique,sadly some of them have died but that’s the same in the wild, you have mortality going on in the wild.
Caz Graham: Wild Justice is very critical of brood management, in fact they call it brood meddling rather than management and they published a report last week saying it is a waste of money. They argue that that money could be spent in other conservation areas and that there isn’t really robust scientific evidence to prove that it’s doing any good.
Mark Cunliffe Lister: The figures speak for themselves in terms of how successful it’s been, so going from hardly any hen harriers now to having hundreds of hen harrier chicks that have been bred through the scheme and through the wild, so in terms of Wild Justice, clearly they’re anti-grouse shooting and that’s their agenda and that’s fine, but as a conservation programme I’d say it’s been an incredible success and very happy to sit down and go through the numbers and compare that with other schemes and we can see, can compare that.
Caz Graham: How would you respond to their claim that really this is just a delaying tactic to put off more stringent and effective measures against those gamekeepers who break the law by either shooting or poisoning birds of prey?
Mark Cunliffe-Lister: Yeah, well it’s clearly not about that and clearly it’s dealing with any conflict there so we’re seeing birds every day flying around grouse moors, with keepers, we’re seeing them on, by tag data, we’re seeing them in the air so clearly any illegal killing is not happening. They would like to say it is but you can see that for your own eyes that it isn’t happening.
Caz Graham: Oh well there is evidence that illegal killing happens, we do report on cases where gamekeepers have been convicted, even, for shooting or for poisoning birds of prey.
Mark Cunliffe-Lister: Yeah, there, sadly do seem to be isolated incidents.
Caz Graham: And where do you see brood management going in the future because some would say it’s not a very sustainable kind of way forward is it?
Mark Cunliffe-Lister: Oh I’d say it’s very sustainable. As I say, we’re clear that there is a conflict between hen harriers and grouse, we’re not hiding away from that and this allows it to be managed, so it’s a job that people came together, decided what the best way forward was, brood management was the way they thought would work best, we put that in to practice, we’ve shown it does work and yeah, I’d say it’s very sustainable moving forwards.
Caz Graham: Mark Cunliffe-Lister from the Moorland Association. We asked Wild Justice to come on this morning’s programme but without seeing more extensive data from Natural England, they declined. Well, Natural England, the Government’s advisor on nature is also a partner in the brood management trial project. John Holmes, a strategy director for Natural England oversees it.
Natural England Strategy Director John Holmes: The purpose of the brood management trial is to test the significance of the availability of brood management to moorland managers in achieving that increase.
Caz Graham: And Natural England lead the monitoring for this project. The Moorland Association tell us that they have reared and released 24 chicks this year, does that figure tally with what you have?
John Holmes: That’s absolutely right, we work alongside them in that work and that’s spot on.
Caz Graham: Can you explain to us who funds this project and how much it’s cost so far?
John Holmes: Part of it is funded by the industry itself through the Moorland Association so actually all the practical work to do brood management is funded by them, release aviaries, buying tags for monitoring and things. Natural England we estimate has spent around £800,000 since the trial started but that will be on things like staff to undertake sound assessment of the science that underlines the licences to allow it to happen and alongside that some work on persecution and investigations.
Caz Graham: £800,000, that sounds like an awful lot really.
John Holmes: Well I would say that sounds good value for recovering of a species that’s been completely extinct. Years and years of way more money than that being spent on investigation but no successful prosecutions whatsoever. We know that illegal persecution goes on and we’re continuing to investigate it. We certainly know that it would cost hundred of thousands for protection of a single nest by the police year round so actually in terms of the increase we’ve got that’s really good value for money.
Caz Graham: Isn’t just cracking down on the criminal element who persecute raptors, birds of prey, isn’t that really where the focus should be?
John Holmes: The simple answer is it hasn’t worked, you know, enforcement was tried and it still goes on, you know, we absolutely back enforcement and work with the police to try and find those criminals but it simply didn’t work. The other thing is to say cracking down on criminals assumes that everybody who manages a moor, or owns a moor, is a criminal and the simple fact is that if landowners and gamekeepers come to us and say, ‘Look, we want to have hen harriers, we want to look after hen harriers’, we’re gonna work with them because the results are clear.
Caz Graham: A point that Wild Justice might well make though is that you’re dealing with a criminal act by perhaps just removing the temptation rather than arresting the perpetrators, you know it’s a bit like ignoring car thieves in an area but paying for a few cars to be stuck in a garage.
John Holmes: I think a better analogy would be to assume that if you’re having your car stolen you’re assuming everyone you meet near your car is gonna steal it and that’s simply not the case.
Caz Graham: I want to put to you another questions as well about Wild Justice’s claims. They say they’re really unimpressed by the standard of scientific enquiry that’s evident in Natural England’s brood management study. How would you respond to that?
John Holmes: Well we’ve got an independent panel that advises us on that science, made up of ornithological and statistical experts, it is a trial, things aren’t always perfect in both the planning and execution, you have to react to real situations on the ground. One of the things we’re trying to measure is how the availability of brood management has influenced people’s opinions of hen harriers and may have resulted in less persecution. That’s really hard to do, it’s not easy to figure out what questions you ask but we’ve got expert social scientists who know how to ask those sorts of questions and we’re still part way through the trial.
Caz Graham: I mean the trial’s been going on for five years, it’s had an extra two years added to it, I mean, gosh, is it still a trial, can you still call it a trial at that length?
John Holmes: It’s still a trial because we don’t actually know the answer to the significance of brood management in achieving the outcome that we’ve got so far.
Caz Graham: So how many years can the trial go on? When will you be able to say whether it does work?
John Holmes: Well it’ll go on until we get a scientifically robust answer. We’re hoping that these next two years will significantly increase our information and lead to some better answers and where we might take hen harrier management in the future.
ENDS